Microalgae colonization of different microplastic polymers in experimental mesocosms across an environmental gradient
- PMID: 34773676
- PMCID: PMC9299714
- DOI: 10.1111/gcb.15989
Microalgae colonization of different microplastic polymers in experimental mesocosms across an environmental gradient
Abstract
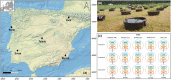
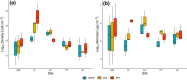
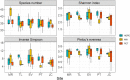
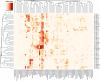
A variety of organisms can colonize microplastic surfaces through biofouling processes. Heterotrophic bacteria tend to be the focus of plastisphere research; however, the presence of epiplastic microalgae within the biofilm has been repeatedly documented. Despite the relevance of biofouling in determining the fate and effects of microplastics in aquatic systems, data about this process are still scarce, especially for freshwater ecosystems. Here, our goal was to evaluate the biomass development and species composition of biofilms on different plastic polymers and to investigate whether plastic substrates exert a strong enough selection to drive species sorting, overcoming other niche-defining factors. We added microplastic pellets of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and a mix of the two polymers in 15 lentic mesocosms in five different locations of the Iberian Peninsula, and after one month, we evaluated species composition and biomass of microalgae developed on plastic surfaces. Our results, based on 45 samples, showed that colonization of plastic surfaces occurred in a range of lentic ecosystems covering a wide geographical gradient and different environmental conditions (e.g., nutrient concentration, conductivity, macrophyte coverage). We highlighted that total biomass differed based on the polymer considered, with higher biomass developed on PET substrate compared to HDPE. Microplastics supported the growth of a rich and diversified community of microalgae (242 species), with some cosmopolite species. However, we did not observe species-specificity in the colonization of the different plastic polymers. Local species pool and nutrient concentration rather than polymeric composition seemed to be the determinant factor defying the community diversity. Regardless of specific environmental conditions, we showed that many species could coexist on the surface of relatively small plastic items, highlighting how microplastics may have considerable carrying capacity, with possible consequences on the wider ecological context.
Keywords: biofouling; epiplastic community; periphyton; phytobenthos; plastic colonization; plastisphere.
© 2021 The Authors. Global Change Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abreu, I. , Ribeiro, H. , & Cunha, M. (2003). An Aeropalynological study of the Porto region (Portugal). Aerobiologia, 19(3), 235–241. 10.1023/B:AERO.0000006573.12721.e6 - DOI
-
- Algarte, V. M. , Siqueira, T. , Landeiro, V. L. , Rodrigues, L. , Bonecker, C. C. , Rodrigues, L. C. , Santana, N. F. , Thomaz, S. M. , & Bini, L. M. (2017). Main predictors of periphyton species richness depend on adherence strategy and cell size. PLoS One, 12(7), e0181720. 10.1371/journal.pone.0181720 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alonso‐Sarría, F. , Martínez‐Hernández, C. , Romero‐Díaz, A. , Cánovas‐García, F. , & Gomariz‐Castillo, F. (2016). Main environmental features leading to recent land abandonment in murcia region (Southeast Spain). Land Degradation & Development, 27(3), 654–670. 10.1002/ldr.2447 - DOI
-
- Amaral‐Zettler, L. A. , Zettler, E. R. , Slikas, B. , Boyd, G. D. , Donald, W. , Morrall, C. E. , Proskurowski, G. , & Mincer, T. J. (2015). The biogeography of the Plastisphere: Implications for policy. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 13(10), 541–546. 10.1890/150017 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

