Mechanisms of Ototoxicity and Otoprotection
- PMID: 34774227
- PMCID: PMC8597902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.otc.2021.08.007
Mechanisms of Ototoxicity and Otoprotection
Abstract
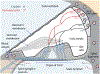
Ototoxicity refers to damage to the inner ear that leads to functional hearing loss or vestibular disorders by selected pharmacotherapeutics as well as a variety of environmental exposures (eg, lead, cadmium, solvents). This article reviews the fundamental mechanisms underlying ototoxicity by clinically relevant, hospital-prescribed medications (ie, aminoglycoside antibiotics or cisplatin, as illustrative examples). Also reviewed are current strategies to prevent prescribed medication-induced ototoxicity, with several clinical or candidate interventional strategies being discussed.
Keywords: Aminoglycosides; Blood-labyrinth barrier; Cochleotoxicity; Ototherapeutics; Ototoxicity monitoring; Platinum-based therapeutics; Vestibulotoxicity.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The author has no conflicts of interests pertinent to this article. This review was supported by National Institutes of Health research awards R01 DC004555 and R01 DC016880, as well as an NIGMS CoBRE Award P20 GM139762 to P.S. Steyger.
Figures
References
-
- Gopal KV, Wu C, Shrestha B, Campbell KC, Moore EJ, Gross GW. d-Methionine protects against cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity in cortical networks. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2012;34(5):495–504. - PubMed
-
- Humes HD. Insights into ototoxicity. Analogies to nephrotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;884:1518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

