Development and Evaluation of a TaqMan Real-Time PCR Assay for the Rapid Detection of Cross-Contamination of RD (Human) and L20B (Mouse) Cell Lines Used in Poliovirus Surveillance
- PMID: 34774617
- PMCID: PMC10898489
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114354
Development and Evaluation of a TaqMan Real-Time PCR Assay for the Rapid Detection of Cross-Contamination of RD (Human) and L20B (Mouse) Cell Lines Used in Poliovirus Surveillance
Abstract
Background: The cross-contamination of cell lines in culture is a persistent problem. Genetically modified L20B (Mouse) and RD (Human Rhabdomyosarcoma) cell lines are commonly used in poliovirus research, surveillance, and diagnostics. Cross-contamination between these cell lines leads to unreproducible results and unreliable surveillance data, negatively affecting public health. The gold standard method for cell authentication is Short Tandem Repeats analysis, which is time-consuming and expensive. The disadvantage of STR is limited detection of interspecies contamination.
Methods: This assay targets the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (MTCO1) gene, a highly conserved and emergent DNA barcode region for detection of cross-contamination in RD and L20B cell lines. The MagNA Pure Compact instrument and ABI 7500 Fast Dx Real-time PCR systems were used for DNA extraction and to perform real-time PCR respectively.
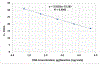
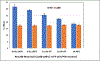
Results: The newly developed assay is very sensitive with a limit of detection of 100 RD cells/1 million L20B/mL. The amplification efficiency and R2-value were 102.26% and 0.9969 respectively. We evaluated specificity of the assay with five human and four mouse cell lines, as well as monkey and rat cell lines. The assay showed no cross-reactivity with genomic DNA from human, mouse, rat, or monkey cell lines. The analytical sensitivity was also evaluated by spiking varying amounts of RD cells (0.001% - 10%) into L20B cells. There was no difference in CT values when running single-plex or duplex PCR reactions with similar experimental conditions.
Conclusions: We have developed and validated a TaqMan real-time PCR assay, a sensitive method for the detection of cross-contamination of RD and L20B cell lines.
Keywords: Cell lines cross-contamination; L20B cells; RD cells; TaqMan Real-time PCR.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
L20B cells simplify culture of polioviruses from clinical samples.J Med Virol. 1999 Jun;58(2):188-92. J Med Virol. 1999. PMID: 10335869
-
Environmental surveillance of polioviruses with special reference to L20B cell line.Virusdisease. 2017 Dec;28(4):383-389. doi: 10.1007/s13337-017-0409-1. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Virusdisease. 2017. PMID: 29291229 Free PMC article.
-
Replacement of primary monkey kidney cells by L20B cell line in the test for effective inactivation of inactivated poliovirus vaccine.J Virol Methods. 2018 Jun;256:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 13. J Virol Methods. 2018. PMID: 29548747
-
Quality Assurance in the Polio Laboratory. Cell Sensitivity and Cell Authentication Assays.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1387:109-27. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3292-4_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26983732
-
[Quantitative PCR in the diagnosis of Leishmania].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):163-7. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305709 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
A new intronic quantitative PCR method led to the discovery of transformation from human ascites to murine malignancy in a mouse model.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 6;13:1062424. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1062424. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36865791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Polio Laboratory Manual. 2004.
-
- CDC. Polio Disease and Poliovirus. https://www.cdc.gov/cpr/polioviruscontainment/diseaseandvirus.htm. 2020.
-
- Dunn G. Quality Assurance in the Polio Laboratory. Cell Sensitivity and Cell Authentication Assays. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1387:109–27. - PubMed
-
- Nejati A, Tabatabaie H, Yousefi M, Mollaei-Kandelous Y, Shahmahmoodi S. Identification of RD and L20B Cell Lines Cross-Contamination by Multiplex SYBR-Green PCR in Poliovirus Laboratory. Iranian Journal of Virology. 2017;11:14–8.
-
- Mendelsohn CL, Wimmer E, Racaniello VR. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989;56:855–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

