Antimicrobial resistance in the globalized food chain: a One Health perspective applied to the poultry industry
- PMID: 34775576
- PMCID: PMC8590523
- DOI: 10.1007/s42770-021-00635-8
Antimicrobial resistance in the globalized food chain: a One Health perspective applied to the poultry industry
Abstract
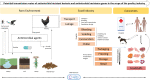
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains a major global public health crisis. The food animal industry will face escalating challenges to increase productivity while minimizing AMR, since the global demand for animal protein has been continuously increasing and food animals play a key role in the global food supply, particularly broiler chickens. As chicken products are sources of low-cost, high-quality protein, poultry production is an important economic driver for livelihood and survival in developed and developing regions. The globalization of the food supply, markedly in the poultry industry, is aligned to the globalization of the whole modern society, with an unprecedented exchange of goods and services, and transit of human populations among regions and countries. Considering the increasing threat posed by AMR, human civilization is faced with a complex, multifaceted problem compromising its future. Actions to mitigate antimicrobial resistance are needed in all sectors of the society at the human, animal, and environmental levels. This review discusses the problems associated with antimicrobial resistance in the globalized food chain, using the poultry sector as a model. We cover critical aspects of the emergence and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in the poultry industry and their implications to public health in a global perspective. Finally, we provide current insights using the multidisciplinary One Health approach to mitigate AMR at the human-animal-environment interface.
Keywords: Aminoglycosides; Broilers; Fluoroquinolones; Gram-negative; Gram-positive; Tetracyclines; β-Lactams.
© 2021. Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ritchie H (2017) Meat and dairy production. Our World Data. Published online 2010
-
- FAO (2020) Meat market review, overview of global meat market developments in 2019
-
- OECD/FAO (2020) Meat. In: OECD-FAO agricultural outlook 2020-2029. OECD Publishing
-
- FAO (2020) Food outlook - biannual report on global food markets – November 2020
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs PD (2019) World population prospects 2019: highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials