Characteristics and Prognosis of Stroke in Living Donor Renal Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 34776472
- PMCID: PMC9444810
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.63189
Characteristics and Prognosis of Stroke in Living Donor Renal Transplant Recipients
Abstract
Aims: We aimed to determine the characteristics and vascular outcomes of stroke in renal transplant (RT) recipients and compare them with those in patients on hemodialysis (HD) and those with no renal replacement therapy (RRT).
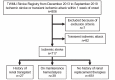
Methods: In this prospective observational study, 717 patients (mean age, 70.8 years; male, 60.5%) with acute ischemic stroke within one week of onset were consecutively enrolled and followed for one year. The patients were classified into three groups: (1) living donor RT recipients (n=27); (2) patients on maintenance HD before the index stroke (n=39); and (3) those with no history of RRT (n=651). The primary outcome was a composite of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
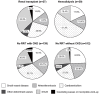
Results: Diabetic nephropathy was the most common reason for RRT in both RT and HD patients. RT patients were more likely to have embolic stroke of undetermined source (33.3%) than others, whereas HD patients more often had cardioembolism (51.3%). No difference was observed in the MACE risk between the patients in RT and non-RRT groups (annual rate, 11.3% vs. 13.1%; log-rank P=0.82; hazard ratio [95% confidence interval], 0.92 [0.29-2.98]). In contrast, HD patients had a greater risk of MACE than those with no RRT (annual rate, 28.2% vs. 13.1%; log-rank P=0.019; hazard ratio [95% confidence interval], 2.24 [1.16-4.3]).
Conclusions: The underlying etiologies of stroke differed in RT and HD patients. The one-year risk of MACE for stroke patients who had received an RT was lower than that for patients undergoing HD and comparable with that of patients with no RRT.
Keywords: Embolic stroke of undetermined source; End stage kidney disease; Hemodialysis; Renal transplantation; Stroke.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[REIN Report 2011--summary].Nephrol Ther. 2013 Sep;9 Suppl 1:S3-6. doi: 10.1016/S1769-7255(13)70036-1. Nephrol Ther. 2013. PMID: 24119584 French.
-
Do the outcomes of living donor renal allograft recipients differ with peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis as a bridge renal replacement therapy?Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2014 Nov;25(6):1202-9. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.144253. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2014. PMID: 25394436
-
Comparative study of renal replacement therapy in Korean diabetic end-stage renal disease patients: a single center study.Yonsei Med J. 2003 Jun 30;44(3):454-62. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2003.44.3.454. Yonsei Med J. 2003. PMID: 12833583
-
Comparison Between Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis in the Risks for Disease Activity in LN-ESRD Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Altern Ther Health Med. 2022 Sep;28(6):144-149. Altern Ther Health Med. 2022. PMID: 35648699
-
End-stage renal care in developing countries: the India experience.Ren Fail. 2004 May;26(3):201-8. doi: 10.1081/jdi-120039516. Ren Fail. 2004. PMID: 15354966 Review.
References
-
- Reese PP, Boudville N, Garg AX. Living kidney donation: outcomes, ethics, and uncertainty. Lancet, 2015; 385: 2003-2013 - PubMed
-
- United States Renal Data System. 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD. 2020
-
- Toyoda K, Fujii K, Fujimi S, Kumai Y, Tsuchimochi H, Ibayashi S, Iida M. Stroke in patients on maintenance hemodialysis: a 22-year single-center study. Am J Kidney Dis, 2005; 45: 1058-1066 - PubMed
-
- Sozio SM, Armstrong PA, Coresh J, Jaar BG, Fink NE, Plantinga LC, Powe NR, Parekh RS. Cerebrovascular disease incidence, characteristics, and outcomes in patients initiating dialysis: the choices for healthy outcomes in caring for ESRD (CHOICE) study. Am J Kidney Dis, 2009; 54: 468-477 - PMC - PubMed

