Quality of Life and a Surveillant Endocannabinoid System
- PMID: 34776851
- PMCID: PMC8581450
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.747229
Quality of Life and a Surveillant Endocannabinoid System
Abstract
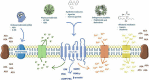
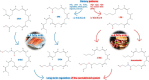
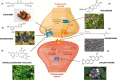
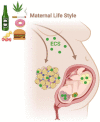
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is an important brain modulatory network. ECS regulates brain homeostasis throughout development, from progenitor fate decision to neuro- and gliogenesis, synaptogenesis, brain plasticity and circuit repair, up to learning, memory, fear, protection, and death. It is a major player in the hypothalamic-peripheral system-adipose tissue in the regulation of food intake, energy storage, nutritional status, and adipose tissue mass, consequently affecting obesity. Loss of ECS control might affect mood disorders (anxiety, hyperactivity, psychosis, and depression), lead to drug abuse, and impact neurodegenerative (Alzheimer's, Parkinson, Huntington, Multiple, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) and neurodevelopmental (autism spectrum) disorders. Practice of regular physical and/or mind-body mindfulness and meditative activities have been shown to modulate endocannabinoid (eCB) levels, in addition to other players as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). ECS is involved in pain, inflammation, metabolic and cardiovascular dysfunctions, general immune responses (asthma, allergy, and arthritis) and tumor expansion, both/either in the brain and/or in the periphery. The reason for such a vast impact is the fact that arachidonic acid, a precursor of eCBs, is present in every membrane cell of the body and on demand eCBs synthesis is regulated by electrical activity and calcium shifts. Novel lipid (lipoxins and resolvins) or peptide (hemopressin) players of the ECS also operate as regulators of physiological allostasis. Indeed, the presence of cannabinoid receptors in intracellular organelles as mitochondria or lysosomes, or in nuclear targets as PPARγ might impact energy consumption, metabolism and cell death. To live a better life implies in a vigilant ECS, through healthy diet selection (based on a balanced omega-3 and -6 polyunsaturated fatty acids), weekly exercises and meditation therapy, all of which regulating eCBs levels, surrounded by a constructive social network. Cannabidiol, a diet supplement has been a major player with anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, antidepressant, and antioxidant activities. Cognitive challenges and emotional intelligence might strengthen the ECS, which is built on a variety of synapses that modify human behavior. As therapeutically concerned, the ECS is essential for maintaining homeostasis and cannabinoids are promising tools to control innumerous targets.
Keywords: BDNF; THC – tetrahydrocannabinol; anandamide; cannabidiol; diet; exercise; meditation; metabolic programming.
Copyright © 2021 de Melo Reis, Isaac, Freitas, de Almeida, Schuck, Ferreira, Andrade-da-Costa and Trevenzoli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abel E. L. (1975). Cannabis: effects on hunger and thirst. Behav. Biol. 15 255–281. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad R., Goffin K., Van Den Stock J., De Winter F. L., Cleeren E., Bormans G., et al. (2014). In vivo type 1 cannabinoid receptor availability in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 24 242–250. - PubMed
-
- Almeida M. M., Dias-Rocha C. P., Reis-Gomes C. F., Wang H., Atella G. C., Cordeiro A., et al. (2019). Maternal high-fat diet impairs leptin signaling and up-regulates type-1 cannabinoid receptor with sex-specific epigenetic changes in the hypothalamus of newborn rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 103 306–315. 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.02.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Almeida M. M., Dias-Rocha C. P., Reis-Gomes C. F., Wang H., Cordeiro A., Pazos-Moura C. C., et al. (2020). Maternal high-fat diet up-regulates type-1 cannabinoid receptor with estrogen signaling changes in a sex- and depot- specific manner in white adipose tissue of adult rat offspring. Eur. J. Nutr. 60 1313–1326. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

