Corticospinal Excitability of the Lower Limb Muscles During the Anticipatory Postural Adjustments: A TMS Study During Dart Throwing
- PMID: 34776899
- PMCID: PMC8580880
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.703377
Corticospinal Excitability of the Lower Limb Muscles During the Anticipatory Postural Adjustments: A TMS Study During Dart Throwing
Abstract
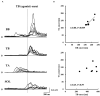
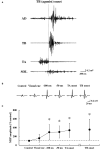
Objective: To investigate whether the changes in the corticospinal excitability contribute to the anticipatory postural adjustments (APAs) in the lower limb muscles when performing the ballistic upper limb movement of the dart throwing. Methods: We examined the primary motor cortex (M1) excitability of the lower limb muscles [tibialis anterior (TA) and soleus (SOL) muscles] during the APA phase by using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) in the healthy volunteers. The surface electromyography (EMG) of anterior deltoid, triceps brachii, biceps brachii, TA, and SOL muscles was recorded and the motor evoked potential (MEP) to TMS was recorded in the TA muscle along with the SOL muscle. TMS at the hotspot of the TA muscle was applied at the timings immediately prior to the TA onset. The kinematic parameters including the three-dimensional motion analysis and center of pressure (COP) during the dart throwing were also assessed. Results: The changes in COP and EMG of the TA muscle occurred preceding the dart throwing, which involved a slight elbow flexion followed by an extension. The correlation analysis revealed that the onset of the TA muscle was related to the COP change and the elbow joint flexion. The MEP amplitude in the TA muscle, but not that in the SOL muscle, significantly increased immediately prior to the EMG burst (100, 50, and 0 ms prior to the TA onset). Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that the corticospinal excitability of the TA muscle increases prior to the ballistic upper limb movement of the dart throwing, suggesting that the corticospinal pathway contributes to the APA in the lower limb in a muscle-specific manner.
Keywords: center of pressure (COP); central command; motor evoked potential (MEP); motor imagery ability; postural control; three-dimensional motion analysis; transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Copyright © 2021 Matsumoto, Liang, Ueda and Irie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
External and internal focus of attention differentially modulate corticospinal excitability in anticipatory postural adjustments.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 26;12(1):22385. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26987-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36572719 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical contributions to anticipatory postural adjustments in the trunk.J Physiol. 2018 Apr 1;596(7):1295-1306. doi: 10.1113/JP275312. Epub 2018 Feb 25. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29368403 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of lower limb muscle corticospinal excitability during various types of motor imagery.Neurosci Lett. 2024 Jan 1;818:137551. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2023.137551. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Neurosci Lett. 2024. PMID: 37926294
-
Anticipatory postural adjustments in older versus young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 23;11(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s13643-022-02116-x. Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36419140 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of corticospinal influence over hand muscles during gripping tasks in man and monkey.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1996 Apr;74(4):547-58. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8828899 Review.
Cited by
-
External and internal focus of attention differentially modulate corticospinal excitability in anticipatory postural adjustments.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 26;12(1):22385. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26987-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36572719 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Cognitive Load on Anticipatory Postural Adjustment Latency and its Relationship with Pain-Related Dysfunction in Non-specific Chronic Low Back Pain: A Cross-Sectional Study.Pain Ther. 2023 Jun;12(3):723-735. doi: 10.1007/s40122-023-00495-0. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Pain Ther. 2023. PMID: 36932302 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dry needling on spasticity, cortical excitability, and range of motion in a patient with multiple sclerosis: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Mar 24;18(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04452-z. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38521912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aloraini S. M., Glazebrook C. M., Pooyania S., Sibley K. M., Singer J., Passmore S. (2020). An external focus of attention compared to an internal focus of attention improves anticipatory postural adjustments among people post-stroke. Gait Posture 82, 100–105. 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2020.08.133 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

