Case Report: Preliminary Images From an Electromagnetic Portable Brain Scanner for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Acute Stroke
- PMID: 34777233
- PMCID: PMC8589013
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.765412
Case Report: Preliminary Images From an Electromagnetic Portable Brain Scanner for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Acute Stroke
Abstract
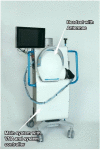
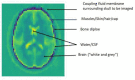
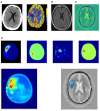
Introduction: Electromagnetic imaging is an emerging technology which promises to provide a mobile, and rapid neuroimaging modality for pre-hospital and bedside evaluation of stroke patients based on the dielectric properties of the tissue. It is now possible due to technological advancements in materials, antennae design and manufacture, rapid portable computing power and network analyses and development of processing algorithms for image reconstruction. The purpose of this report is to introduce images from a novel, portable electromagnetic scanner being trialed for bedside and mobile imaging of ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke. Methods: A prospective convenience study enrolled patients (January 2020 to August 2020) with known stroke to have brain electromagnetic imaging, in addition to usual imaging and medical care. The images are obtained by processing signals from encircling transceiver antennae which emit and detect low energy signals in the microwave frequency spectrum between 0.5 and 2.0 GHz. The purpose of the study was to refine the imaging algorithms. Results: Examples are presented of haemorrhagic and ischaemic stroke and comparison is made with CT, perfusion and MRI T2 FAIR sequence images. Conclusion: Due to speed of imaging, size and mobility of the device and negligible environmental risks, development of electromagnetic scanning scanner provides a promising additional modality for mobile and bedside neuroimaging.
Keywords: electromagnetic neuroimaging; electromagnetic stroke imaging; mobile brain scanner; mobile neuroimaging; mobile stroke imaging.
Copyright © 2021 Cook, Brown, Widanapathirana, Shah, Walsham, Trakic, Zhu, Zamani, Guo, Brankovic, Al-Saffar, Stancombe, Bialkowski, Nguyen, Bialkowski, Crozier and Abbosh.
Conflict of interest statement
AA, KB, ABi, SC, LG, PN, AZ, and GZ are authors of relevant patents. SC, KB, DC, and JW have non-executive or advisory positions with EMVision. SC, DC, DS, and JW are shareholders in EMVision. AA-S, LG, PN, AS, IW, AZ, and GZ are part funded by EMVision. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The research was conducted to refine and develop the imaging technology. The authors declare that this study received funding from EMVision, Sydney, with involvement in the design, manufacture and supply of the device, the study design and analysis of the data.
Figures

References
-
- Brankovic A, Zamani A, Trakic A, Bialkowski K, Mohammed B, Cook D, et al. . Unsupervised algorithm for brain anomalies localization in electromagnetic imaging. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging. (2020) 6:1595–606. 10.1109/TCI.2020.3041922 - DOI
-
- Trakic A, Brankovic A, Zamani A, Nguyen-Trong N, Mohammed B, Stancombe A, et al. . Expedited Stroke Imaging With Electromagnetic Polar Sensitivity Encoding. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. (2020) 68:8072–81. 10.1109/TAP.2020.2996810 - DOI
-
- Zhu G, Bialkowski A, Guo L, Mohammed B, Abbosh A. Stroke classification in simulated electromagnetic imaging using graph approaches. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. (2021) 5:46–53. 10.1109/JERM.2020.2995329 - DOI
-
- Emberson J, Lees KR, Lyden P, Blackwell L, Albers G, Bluhmki E, et al. . Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet. (2014) 384:1929–35. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60584-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

