Novel Enzymes From the Red Sea Brine Pools: Current State and Potential
- PMID: 34777282
- PMCID: PMC8578733
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.732856
Novel Enzymes From the Red Sea Brine Pools: Current State and Potential
Abstract
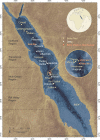
The Red Sea is a marine environment with unique chemical characteristics and physical topographies. Among the various habitats offered by the Red Sea, the deep-sea brine pools are the most extreme in terms of salinity, temperature and metal contents. Nonetheless, the brine pools host rich polyextremophilic bacterial and archaeal communities. These microbial communities are promising sources for various classes of enzymes adapted to harsh environments - extremozymes. Extremozymes are emerging as novel biocatalysts for biotechnological applications due to their ability to perform catalytic reactions under harsh biophysical conditions, such as those used in many industrial processes. In this review, we provide an overview of the extremozymes from different Red Sea brine pools and discuss the overall biotechnological potential of the Red Sea proteome.
Keywords: Red Sea; biocatalysis; brine pools; extremophile; extremozymes.
Copyright © 2021 Renn, Shepard, Vancea, Karan, Arold and Rueping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sedimentary porewaters record regional tectonic and climate events that perturbed a deep-sea brine pool in the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Feb 20;912:168804. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168804. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38036117
-
Cold and Hot Extremozymes: Industrial Relevance and Current Trends.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 Oct 20;3:148. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00148. eCollection 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26539430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Red Sea Brine Pool Specialized Metabolism Gene Clusters Encoding Potential Metabolites for Biotechnological Applications and Extremophile Survival.Mar Drugs. 2019 May 8;17(5):273. doi: 10.3390/md17050273. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31071993 Free PMC article.
-
Insertion sequences enrichment in extreme Red sea brine pool vent.Extremophiles. 2017 Mar;21(2):271-282. doi: 10.1007/s00792-016-0900-4. Epub 2016 Dec 3. Extremophiles. 2017. PMID: 27915389
-
Marine extremophiles: a source of hydrolases for biotechnological applications.Mar Drugs. 2015 Apr 3;13(4):1925-65. doi: 10.3390/md13041925. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25854643 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the taxonomic and functional diversity of marine benthic micro-Eukaryotes along the Red Sea coast of Jeddah city.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Aug;29(8):103342. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103342. Epub 2022 Jun 26. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35846388 Free PMC article.
-
The exceptionally efficient quorum quenching enzyme LrsL suppresses Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm production.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 22;13:977673. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.977673. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36071959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler-Nissen J. (1982). Limited enzymic degradation of proteins: a new approach in the industrial application of hydrolases. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 32 138–156.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

