An Stomatin, Prohibitin, Flotillin, and HflK/C-Domain Protein Required to Link the Phage-Shock Protein to the Membrane in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 34777311
- PMCID: PMC8581546
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.754924
An Stomatin, Prohibitin, Flotillin, and HflK/C-Domain Protein Required to Link the Phage-Shock Protein to the Membrane in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
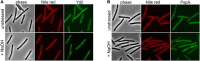
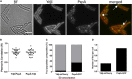
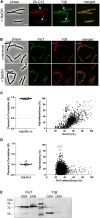
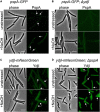
Membrane surveillance and repair is of utmost importance to maintain cellular integrity and allow cellular life. Several systems detect cell envelope stress caused by antimicrobial compounds and abiotic stresses such as solvents, pH-changes and temperature in bacteria. Proteins containing an Stomatin, Prohibitin, Flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH)-domain, including bacterial flotillins have been shown to be involved in membrane protection and membrane fluidity regulation. Here, we characterize a bacterial SPFH-domain protein, YdjI that is part of a stress induced complex in Bacillus subtilis. We show that YdjI is required to localize the ESCRT-III homolog PspA to the membrane with the help of two membrane integral proteins, YdjG/H. In contrast to classical flotillins, YdjI resides in fluid membrane regions and does not enrich in detergent resistant membrane fractions. However, similarly to FloA and FloT from B. subtilis, deletion of YdjI decreases membrane fluidity. Our data reveal a hardwired connection between phage shock response and SPFH proteins.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; SPFH-domain proteins; YdjI; cell envelope stress response; flotillins; phage-shock protein.
Copyright © 2021 Scholz, Baur, Wolf and Bramkamp.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthetic motility and cell shape defects associated with deletions of flotillin/reggie paralogs in Bacillus subtilis and interplay of these proteins with NfeD proteins.J Bacteriol. 2012 Sep;194(17):4652-61. doi: 10.1128/JB.00910-12. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22753055 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial targeting of Candida albicans SPFH proteins and requirement of stomatins for SDS-induced stress tolerance.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jan 7;13(1):e0173324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01733-24. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39641539 Free PMC article.
-
The lipid raft markers stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH)-domain proteins form an operon with NfeD proteins and function with apolar polyisoprenoid lipids.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020 Feb;46(1):38-48. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2020.1716682. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31983249 Review.
-
Bacterial flotillins as destabilizers of phospholipid membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2025 Jan;1867(1):184399. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2024.184399. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2025. PMID: 39521105
-
Flotillins in membrane trafficking and physiopathology.Biol Cell. 2025 Jan;117(1):e2400134. doi: 10.1111/boc.202400134. Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 39877933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cyanobacterial membrane dynamics in the light of eukaryotic principles.Biosci Rep. 2023 Feb 27;43(2):BSR20221269. doi: 10.1042/BSR20221269. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36602300 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity, origin, and evolution of the ESCRT systems.mBio. 2024 Mar 13;15(3):e0033524. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00335-24. Epub 2024 Feb 21. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38380930 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible conjugation of a CBASS nucleotide cyclase regulates bacterial immune response to phage infection.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Jun;9(6):1579-1592. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01670-5. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38589469 Free PMC article.
-
BacA: a possible regulator that contributes to the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 5;15:1332448. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1332448. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38505547 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity, Origin and Evolution of the ESCRT Systems.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 7:2024.02.06.579148. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.06.579148. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mBio. 2024 Mar 13;15(3):e0033524. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00335-24. PMID: 38903064 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

