Highly Purified Alloantigen-Specific Tregs From Healthy and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Can Be Long-Term Expanded, Maintaining a Suppressive Phenotype and Function in the Presence of Inflammatory Cytokines
- PMID: 34777330
- PMCID: PMC8581357
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.686530
Highly Purified Alloantigen-Specific Tregs From Healthy and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Can Be Long-Term Expanded, Maintaining a Suppressive Phenotype and Function in the Presence of Inflammatory Cytokines
Abstract
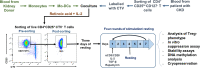
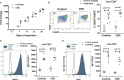
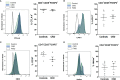
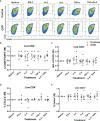
The adoptive transfer of alloantigen-specific regulatory T cells (alloTregs) has been proposed as a therapeutic alternative in kidney transplant recipients to the use of lifelong immunosuppressive drugs that cause serious side effects. However, the clinical application of alloTregs has been limited due to their low frequency in peripheral blood and the scarce development of efficient protocols to ensure their purity, expansion, and stability. Here, we describe a new experimental protocol that allows the long-term expansion of highly purified allospecific natural Tregs (nTregs) from both healthy controls and chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, which maintain their phenotype and suppressive function under inflammatory conditions. Firstly, we co-cultured CellTrace Violet (CTV)-labeled Tregs from CKD patients or healthy individuals with allogeneic monocyte-derived dendritic cells in the presence of interleukin 2 (IL-2) and retinoic acid. Then, proliferating CD4+CD25hiCTV- Tregs (allospecific) were sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and polyclonally expanded with anti-CD3/CD28-coated beads in the presence of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), IL-2, and rapamycin. After 4 weeks, alloTregs were expanded up to 2,300 times the initial numbers with a purity of >95% (CD4+CD25hiFOXP3+). The resulting allospecific Tregs showed high expressions of CTLA-4, LAG-3, and CD39, indicative of a highly suppressive phenotype. Accordingly, expanded alloTregs efficiently suppressed T-cell proliferation in an antigen-specific manner, even in the presence of inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-6, or TNF-α). Unexpectedly, the long-term expansion resulted in an increased methylation of the specific demethylated region of Foxp3. Interestingly, alloTregs from both normal individuals and CKD patients maintained their immunosuppressive phenotype and function after being expanded for two additional weeks under an inflammatory microenvironment. Finally, phenotypic and functional evaluation of cryopreserved alloTregs demonstrated the feasibility of long-term storage and supports the potential use of this cellular product for personalized Treg therapy in transplanted patients.
Keywords: allospecific; expansion; regulatory T cells; suppression; transplantation.
Copyright © 2021 Cortés-Hernández, Alvarez-Salazar, Arteaga-Cruz, Rosas-Cortina, Linares, Alberú Gómez and Soldevila.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Highly purified and functionally stable in vitro expanded allospecific Tr1 cells expressing immunosuppressive graft-homing receptors as new candidates for cell therapy in solid organ transplantation.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 24;14:1062456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1062456. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911743 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Generation of Human Allospecific Induced Tregs With Functional Stability for Use in Immunotherapy in Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 2;11:375. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00375. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32300340 Free PMC article.
-
Natural regulatory T cells from patients with end-stage renal disease can be used for large-scale generation of highly suppressive alloantigen-specific Tregs.Kidney Int. 2017 May;91(5):1203-1213. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.09.043. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 27988212
-
Alloantigen specific T regulatory cells in transplant tolerance.Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 May;9(5):570-4. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2009.01.016. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19539571 Review.
-
Dendritic cells expand antigen-specific Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells including suppressors of alloreactivity.Immunol Rev. 2006 Aug;212:314-29. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00422.x. Immunol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16903923 Review.
Cited by
-
Gentamicin promoted the production of CD4+CD25+ Tregs via the STAT5 signaling pathway in mice sepsis.BMC Immunol. 2022 Sep 26;23(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12865-022-00521-4. BMC Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36162982 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Demethylation of FOXP3-TSDR Enhances the Suppressive Capacity of STAT6-deficient Inducible T Regulatory Cells.Inflammation. 2024 Dec;47(6):2159-2172. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02031-4. Epub 2024 May 3. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38700792 Free PMC article.
-
Highly purified and functionally stable in vitro expanded allospecific Tr1 cells expressing immunosuppressive graft-homing receptors as new candidates for cell therapy in solid organ transplantation.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 24;14:1062456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1062456. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911743 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T-cell dysfunction and its implication for cell therapy.Clin Exp Immunol. 2023 Jul 5;213(1):40-49. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad051. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37158407 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the microenvironment and survival in kidney transplantation: a bibliometric analysis from 2013 to 2023.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 26;15:1379742. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1379742. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38596670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vaidya SR, Aeddula NR. Chronic Renal Failure. Treasure Island (FL: StatPearls; (2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

