Maternal, Decidual, and Neonatal Lymphocyte Composition Is Affected in Pregnant Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 34777345
- PMCID: PMC8585145
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.735564
Maternal, Decidual, and Neonatal Lymphocyte Composition Is Affected in Pregnant Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
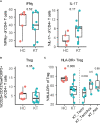
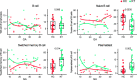
Pregnancy after renal transplantation is associated with an increased risk of complications. While a delicately balanced uterine immune system is essential for a successful pregnancy, little is known about the uterine immune environment of pregnant kidney transplant recipients. Moreover, children born to kidney transplant recipients are exposed in utero to immunosuppressive drugs, with possible consequences for neonatal outcomes. Here, we defined the effects of kidney transplantation on the immune cell composition during pregnancy with a cohort of kidney transplant recipients as well as healthy controls with uncomplicated pregnancies. Maternal immune cells from peripheral blood were collected during pregnancy as well as from decidua and cord blood obtained after delivery. Multiparameter flow cytometry was used to identify and characterize populations of cells. While systemic immune cell frequencies were altered in kidney transplant patients, immune cell dynamics over the course of pregnancy were largely similar to healthy women. In the decidua of women with a kidney transplant, we observed a decreased frequency of HLA-DR+ Treg, particularly in those treated with tacrolimus versus those that were treated with azathioprine next to tacrolimus, or with azathioprine alone. In addition, both the innate and adaptive neonatal immune system of children born to kidney transplant recipients was significantly altered compared to neonates born from uncomplicated pregnancies. Overall, our findings indicate a significant and distinct impact on the maternal systemic, uterine, and neonatal immune cell composition in pregnant kidney transplant recipients, which could have important consequences for the incidence of pregnancy complications, treatment decisions, and the offspring's health.
Keywords: decidua; kidney transplantation; neonatal immunity; pregnancy; renal transplantation; uterine immunity.
Copyright © 2021 Feyaerts, Gillard, van Cranenbroek, Rigodanzo Marins, Baghdady, Comitini, Lely, van Hamersvelt, van der Heijden, Joosten and van der Molen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Outcomes of Children with Fetal and Lactation Immunosuppression Exposure Born to Female Transplant Recipients.Paediatr Drugs. 2022 Sep;24(5):483-497. doi: 10.1007/s40272-022-00525-y. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Paediatr Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35870080 Review.
-
Immunophenotypic profile and increased risk of hospital admission for infection in infants born to female kidney transplant recipients.Am J Transplant. 2015 Jun;15(6):1654-65. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13143. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Am J Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25833197
-
Severe B cell depletion in newborns from renal transplant mothers taking immunosuppressive agents.Transplantation. 1994 Jun 15;57(11):1617-21. Transplantation. 1994. PMID: 8009597
-
Fetal endothelial colony-forming cell impairment after maternal kidney transplantation.Pediatr Res. 2023 Mar;93(4):810-817. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02165-x. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 35732823 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy and the kidney transplant recipient.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2017 Nov;26(6):494-500. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000363. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28985190 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of In Utero Exposure to Maternal Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Immunomodulators on Infant Immune System Development and Function.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;16(1):165-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.03.005. Epub 2023 Mar 25. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36972763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcomes of Children with Fetal and Lactation Immunosuppression Exposure Born to Female Transplant Recipients.Paediatr Drugs. 2022 Sep;24(5):483-497. doi: 10.1007/s40272-022-00525-y. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Paediatr Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35870080 Review.
References
-
- Piccoli GB, Cabiddu G, Daidone G, Guzzo G, Maxia S, Ciniglio I, et al. . The Children of Dialysis: Live-Born Babies From on-Dialysis Mothers in Italy–an Epidemiological Perspective Comparing Dialysis, Kidney Transplantation and the Overall Population. Nephrology Dialysis Transplant Off Publ Eur Dialysis Transplant Assoc - Eur Renal Assoc (2014) 29:1578–86. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfu092 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

