The Role of HDAC6 in Autophagy and NLRP3 Inflammasome
- PMID: 34777380
- PMCID: PMC8578992
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.763831
The Role of HDAC6 in Autophagy and NLRP3 Inflammasome
Abstract
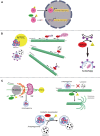
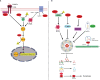
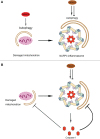
Autophagy fights against harmful stimuli and degrades cytosolic macromolecules, organelles, and intracellular pathogens. Autophagy dysfunction is associated with many diseases, including infectious and inflammatory diseases. Recent studies have identified the critical role of the NACHT, LRR, and PYD domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasomes activation in the innate immune system, which mediates the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β/IL-18 and cleaves Gasdermin D to induce pyroptosis in response to pathogenic and sterile stimuli. Accumulating evidence has highlighted the crosstalk between autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome in multifaceted ways to influence host defense and inflammation. However, the underlying mechanisms require further clarification. Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is a class IIb deacetylase among the 18 mammalian HDACs, which mainly localizes in the cytoplasm. It is involved in two functional deacetylase domains and a ubiquitin-binding zinc finger domain (ZnF-BUZ). Due to its unique structure, HDAC6 regulates various physiological processes, including autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome, and may play a role in the crosstalk between them. In this review, we provide insight into the mechanisms by which HDAC6 regulates autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome and we explored the possibility and challenges of HDAC6 in the crosstalk between autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome. Finally, we discuss HDAC6 inhibitors as a potential therapeutic approach targeting either autophagy or NLRP3 inflammasome as an anti-inflammatory strategy, although further clarification is required regarding their crosstalk.
Keywords: HDAC6; NLRP3 inflammasome; autophagy; inflammation; post-translational modification.
Copyright © 2021 Chang, Li, Hu, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

