A novel data augmentation based on Gabor filter and convolutional deep learning for improving the classification of COVID-19 chest X-Ray images
- PMID: 34777557
- PMCID: PMC8576144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103326
A novel data augmentation based on Gabor filter and convolutional deep learning for improving the classification of COVID-19 chest X-Ray images
Abstract
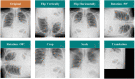
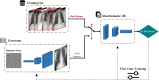
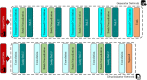
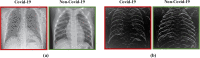
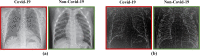
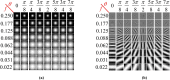
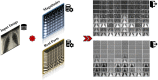
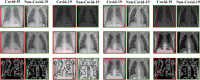
A dangerous infectious disease of the current century, the COVID-19 has apparently originated in a city in China and turned into a widespread pandemic within a short time. In this paper, a novel method has been presented for improving the screening and classification of COVID-19 patients based on their chest X-Ray (CXR) images. This method eliminates the severe dependence of the deep learning models on large datasets and the deep features extracted from them. In this approach, we have not only resolved the data limitation problem by combining the traditional data augmentation techniques with the generative adversarial networks (GANs), but also have enabled a deeper extraction of features by applying different filter banks such as the Sobel, Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) and the Gabor filters. To verify the satisfactory performance of the proposed approach, it was applied on several deep transfer models and the results in each step were compared with each other. For training the entire models, we used 4560 CXR images of various patients with the viral, bacterial, fungal, and other diseases; 360 of these images are in the COVID-19 category and the rest belong to the non-COVID-19 diseases. According to the results, the Gabor filter bank achieves the highest growth in the values of the defined evaluation criteria and in just 45 epochs, it is able to elevate the accuracy by up to 32%. We then applied the proposed model on the DenseNet-201 model and compared its performance in terms of the detection accuracy with the performances of 10 existing COVID-19 detection techniques. Our approach was able to achieve an accuracy of 98.5% in the two-class classification procedure; which makes it a state-of-the-art method for detecting the COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Classification; Data augmentation; Deep learning; Gabor; Generative adversarial network.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Li Q., Guan X., Wu P., Wang X., Zhou L., Tong Y., Ren R., Leung K.S.M., Lau E.H.Y., Wong J.Y., Xing X., Xiang N., Wu Y., Li C., Chen Q.i., Li D., Liu T., Zhao J., Liu M., Tu W., Chen C., Jin L., Yang R., Wang Q.i., Zhou S., Wang R., Liu H., Luo Y., Liu Y., Shao G.e., Li H., Tao Z., Yang Y., Deng Z., Liu B., Ma Z., Zhang Y., Shi G., Lam T.T.Y., Wu J.T., Gao G.F., Cowling B.J., Yang B.o., Leung G.M., Feng Z. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382(13):1199–1207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holshue M.L., DeBolt C., Lindquist S., Lofy K.H., Wiesman J., Bruce H., Spitters C., Ericson K., Wilkerson S., Tural A., Diaz G., Cohn A., Fox LeAnne, Patel A., Gerber S.I., Kim L., Tong S., Lu X., Lindstrom S., Pallansch M.A., Weldon W.C., Biggs H.M., Uyeki T.M., Pillai S.K. novel coronavirus in the United States”. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382(10):929–936. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001191. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- ’worldometer’, COVID-19 CORONAVIRUS / CASES; June, 2021, Available at: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/.
-
- M.A. Jahangir, A. Muheem, M.F. Rizvi, Coronavirus (COVID-19): history, current knowledge and pipeline medications, Int. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020; 4 140. doi: 10.31531/2581, vol. 3080, no. 2, 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
