Prognostic Role of the C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio in Patients With Gynecological Cancers: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34778051
- PMCID: PMC8581351
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.737155
Prognostic Role of the C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio in Patients With Gynecological Cancers: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Many studies have investigated the prognostic role of the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio (CRP/Alb ratio) in patients with gynecological cancers; however, there is lack of consensus owing to conflicting results across studies. We performed a meta-analysis to determine the prognostic role of the CRP/Alb ratio in gynecological cancers.
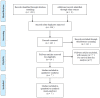
Methods: We searched the PubMed, Embase, the Web of Science, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and Wanfang electronic databases since inception to April 2021. Combined hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to estimate the prognostic effect of the CRP/Alb ratio in gynecological cancers. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) and 95% CIs were used to investigate the association between the CRP/Alb ratio and clinicopathological features.
Results: The meta-analysis included seven studies with 1,847 patients. The pooled results showed that a high pretreatment CRP/Alb ratio was associated with poor overall survival (HR, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.41-2.40; p < 0.001) and progression-/disease-free survival (HR, 2.58; 95% CI, 1.42-4.68; p = 0.002). Additionally, a high CRP/Alb ratio was significantly associated with stages III-IV disease (the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics classification) (OR, 2.98; 95% CI, 1.45-6.14; p = 0.003). However, we observed a non-significant correlation between the CRP/Alb ratio and lymph node metastasis, tumor size, and histopathological grade.
Conclusions: The CRP/Alb ratio is a convenient and accurate predictor of survival outcomes in gynecological cancers. A high CRP/Alb ratio also predicts tumor progression.
Keywords: CRP/Alb ratio; gynecological cancers; meta-analysis; prognostic; risk factors.
Copyright © 2021 Fang, Zheng and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The prognostic value of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2018 Nov 13;38(6):BSR20180686. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180686. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30352836 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio in Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Nutr Cancer. 2021;73(10):1864-1871. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2020.1817510. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Nutr Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32940549
-
Prognostic value of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in predicting overall survival of Chinese cervical cancer patients overall survival: comparison among various inflammation based factors.J Cancer. 2018 Apr 27;9(10):1877-1884. doi: 10.7150/jca.23320. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29805715 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of C-reactive protein in patients with bladder cancer: a meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2445781. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2445781. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39746669 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of C-reactive protein in patients with ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Jan 3;22(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03290-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38172843 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Role of Pretreatment C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio in Urological Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 11;12:879803. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.879803. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35480099 Free PMC article.
-
Survival Predictors in Obstructive Colorectal Cancer: A Combined Clinical, Inflammatory, and Histopathological Approach.In Vivo. 2025 Jul-Aug;39(4):2419-2428. doi: 10.21873/invivo.14041. In Vivo. 2025. PMID: 40578999 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor expression of CXCL12 and survival of patients with colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis.Oncol Lett. 2022 Oct 21;24(6):436. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13556. eCollection 2022 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36420080 Free PMC article.
-
Association of blood group types and clinico-pathological features of gynecological cancers (GCs).BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 23;25(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13527-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39849419 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective: Implications of Docosahexaenoic Acid and Eicosapentaenoic Acid Supplementation on the Immune System during Cancer Chemotherapy: Perspectives from Current Clinical Evidence.Adv Nutr. 2025 Aug;16(8):100464. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2025.100464. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Adv Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40523478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

