CXCL13 Is an Indicator of Germinal Center Activity and Alloantibody Formation Following Transplantation
- PMID: 34778545
- PMCID: PMC8580198
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001247
CXCL13 Is an Indicator of Germinal Center Activity and Alloantibody Formation Following Transplantation
Abstract
Donor-specific antibodies (DSA) are a recognized cause of allograft injury, yet biomarkers that indicate their development posttransplant or guide management are not available. CXCL13 (chemokine [C-X-C motif] ligand 1) is a chemoattractant produced within secondary lymphoid organs necessary for germinal center (GC) and alloantibody formation. Perturbations in serum CXCL13 levels have been associated with humoral immune activity. Therefore, CXCL13 may correlate with the formation of HLA antibodies following transplantation.
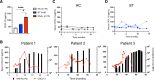
Methods: A murine skin graft model was utilized to define the production and kinetics of CXCL13 in response to alloantigen. Human Tfh:B-cell in vitro cocultures were performed to evaluate CXCL13 production by human lymphocytes, and serum from healthy controls and human transplant recipients with and without de novo DSA was tested for CXCL13.
Results: CXCL13 was detectable in the blood of allografted mice and correlated with Tfh and GC B-cell responses. Greater CXCL13 expression was observed in the draining lymph nodes of allografted mice as compared with naïve or syngeneic graft recipients, and serum levels preceded the detection of DSA posttransplant. Similarly, productive human Tfh:B-cell interactions that led to plasmablast differentiation and IgG formation also exhibited CXCL13 expression. CXCL13 levels in human transplant recipients with de novo DSA were greater than in healthy controls and stable transplant patients and also correlated with the development of alloantibodies in a small cohort of serially monitored recipients.
Conclusions: CXCL13 indicates GC alloreactivity and alloantibody formation and correlated with DSA formation in kidney transplant recipients, thereby introducing CXCL13 as a potential biomarker for HLA antibodies.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Transplantation Direct. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no funding or conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wiebe C, Gibson IW, Blydt-Hansen TD, et al. . Evolution and clinical pathologic correlations of de novo donor-specific HLA antibody post kidney transplant. Am J Transplant. 2012;12:1157–1167. - PubMed
-
- Loupy A, Hill GS, Jordan SC. The impact of donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies on late kidney allograft failure. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:348–357. - PubMed
-
- Hart A, Smith JM, Skeans MA, et al. . OPTN/SRTR 2018 annual data report: kidney. Am J Transplant. 2020;20 (Suppl s1):20–130. - PubMed
-
- Sellarés J, de Freitas DG, Mengel M, et al. . Understanding the causes of kidney transplant failure: the dominant role of antibody-mediated rejection and nonadherence. Am J Transplant. 2012;12:388–399. - PubMed
-
- Bray RA, Gebel HM. Monitoring after renal transplantation: recommendations and caveats. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2008;4:658–659. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

