Global Wheat Head Detection 2021: An Improved Dataset for Benchmarking Wheat Head Detection Methods
- PMID: 34778804
- PMCID: PMC8548052
- DOI: 10.34133/2021/9846158
Global Wheat Head Detection 2021: An Improved Dataset for Benchmarking Wheat Head Detection Methods
Abstract
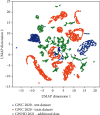
The Global Wheat Head Detection (GWHD) dataset was created in 2020 and has assembled 193,634 labelled wheat heads from 4700 RGB images acquired from various acquisition platforms and 7 countries/institutions. With an associated competition hosted in Kaggle, GWHD_2020 has successfully attracted attention from both the computer vision and agricultural science communities. From this first experience, a few avenues for improvements have been identified regarding data size, head diversity, and label reliability. To address these issues, the 2020 dataset has been reexamined, relabeled, and complemented by adding 1722 images from 5 additional countries, allowing for 81,553 additional wheat heads. We now release in 2021 a new version of the Global Wheat Head Detection dataset, which is bigger, more diverse, and less noisy than the GWHD_2020 version.
Copyright © 2021 Etienne David et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Sambasivan N., Kapania S., Highfill H., Akrong D., Paritosh P., Aroyo L. M. Everyone wants to do the model work, not the data work: data cascades in high-stakes AI. New York, NY, USA: 2021. - DOI
-
- Deng J., Dong W., Socher R., Li L.-J., Li K., Fei-Fei L. ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2009; pp. 248–255.
-
- Lin T.-Y., et al. Microsoft coco: common objects in context. European conference on computer vision. 2014. pp. 740–755.
-
- Cruz J. A., Yin X., Liu X., et al. Multi-modality imagery database for plant phenotyping. Machine Vision and Applications. 2016;27(5):735–749. doi: 10.1007/s00138-015-0734-6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

