Digitization and Analysis of Capnography Using Image Processing Technique
- PMID: 34778867
- PMCID: PMC8585923
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2021.723204
Digitization and Analysis of Capnography Using Image Processing Technique
Abstract
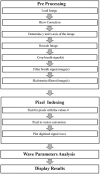
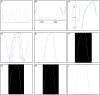
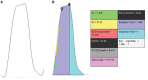
The study of carbon dioxide expiration is called capnometry. The graphical representation of capnometry is called capnography. There is a growing interest in the usage of capnography as the usage has expanded toward the study of metabolism, circulation, lung perfusion and diffusion, quality of spontaneous respiration, and patency of airways outside of its typical usage in the anesthetic and emergency medicine field. The parameters of the capnograph could be classified as carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration and time points and coordinates, slopes angle, volumetric studies, and functional transformation of wave data. Up to date, there is no gold standard device for the calculation of the capnographic parameters. Capnography digitization using the image processing technique could serve as an option. From the algorithm we developed, eight identical breath waves were tested by four investigators. The values of the parameters chosen showed no significant difference between investigators. Although there were no significant differences between any of the parameters tested, there were a few related parameters that were not calculable. Further testing after refinement of the algorithm could be done. As more capnographic parameters are being derived and rediscovered by clinicians and researchers alike for both lung and non-lung-related diseases, there is a dire need for data analysis and interpretation. Although the proposed algorithm still needs minor refinements and further large-scale testing, we proposed that the digitization of the capnograph via image processing technique could serve as an intellectual option as it is fast, convenient, easy to use, and efficient.
Keywords: EtCO2; capnography; capnometry; end tidal carbon dioxide; time based capnography.
Copyright © 2021 Vijayam, Supriyanto and Malarvili.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of sidestream end-tidal capnography in ventilated infants on the neonatal unit.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 Jun;55(6):1468-1473. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24738. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020. PMID: 32187888
-
Breath emulator for simulation and modelling of expired tidal breath carbon dioxide characteristics.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Mar;200:105826. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105826. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 33187733
-
Capnometry in spontaneously breathing patients: the influence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and expiration maneuvers.Med Sci Monit. 2008 Sep;14(9):CR485-92. Med Sci Monit. 2008. PMID: 18758420
-
Clinical use of volumetric capnography in mechanically ventilated patients.J Clin Monit Comput. 2020 Feb;34(1):7-16. doi: 10.1007/s10877-019-00325-9. Epub 2019 May 31. J Clin Monit Comput. 2020. PMID: 31152285 Review.
-
[Non-invasive patient monitoring in veterinary medicine: pulse oximetry and capnography. II. Capnography].Tierarztl Prax. 1995 Feb;23(1):1-16. Tierarztl Prax. 1995. PMID: 7792768 Review. German.
References
-
- Gravenstein J, Jaffe M, Gravenstein N, Paulus D. Capnography. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; (2011). 10.1017/CBO9780511933837 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

