Using Digital Speech Assessments to Detect Early Signs of Cognitive Impairment
- PMID: 34778869
- PMCID: PMC8579012
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2021.749758
Using Digital Speech Assessments to Detect Early Signs of Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
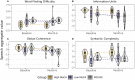
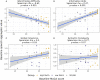
Detecting early signs of cognitive decline is crucial for early detection and treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. Most of the current screening tools for Alzheimer's Disease represent a significant burden, requiring invasive procedures, or intensive and costly clinical testing. Recent findings have highlighted changes to speech and language patterns that occur in Alzheimer's Disease, and may be detectable prior to diagnosis. Automated tools to assess speech have been developed that can be used on a smartphone or tablet, from one's home, in under 10 min. In this study, we present the results of a study of older adults who completed a digital speech assessment task over a 6-month period. Participants were grouped according to those who scored above (N = 18) or below (N = 18) the recommended threshold for detecting cognitive impairment on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and those with diagnoses of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or early Alzheimer's Disease (AD) (N = 14). Older adults who scored above the MoCA threshold had better performance on speech composites reflecting language coherence, information richness, syntactic complexity, and word finding abilities. Those with MCI and AD showed more rapid decline in the coherence of language from baseline to 6-month follow-up, suggesting that this score may be useful both for detecting cognitive decline and monitoring change over time. This study demonstrates that automated speech assessments have potential as sensitive tools to detect early signs of cognitive impairment and monitor progression over time.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; digital biomarker; language; mild cognitive impairment; speech.
Copyright © 2021 Robin, Xu, Kaufman and Simpson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this article are employees of Winterlight Labs.
Figures
References
-
- Gold M, Amatniek J, Carrillo MC, Cedarbaum JM, Hendrix JA, Miller BB, et al. . Digital technologies as biomarkers, clinical outcomes assessment, and recruitment tools in Alzheimer's disease clinical trials. Alzheimers Dement Transl Res Clin Interv. (2018) 4:234–42. 10.1016/j.trci.2018.04.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piau A, Wild K, Mattek N, Kaye J. Current state of digital biomarker technologies for real-life, home-based monitoring of cognitive function for mild cognitive impairment to mild Alzheimer disease and implications for clinical care: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. (2019) 21:e12785. 10.2196/12785 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

