Point-of-care diagnostics: recent developments in a pandemic age
- PMID: 34778896
- PMCID: PMC8860149
- DOI: 10.1039/d1lc00627d
Point-of-care diagnostics: recent developments in a pandemic age
Abstract
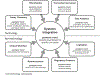
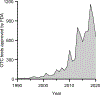
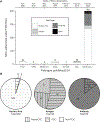
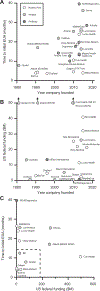
In this review, we provide an overview of developments in point-of-care (POC) diagnostics during the COVID-19 pandemic. We review these advances within the framework of a holistic POC ecosystem, focusing on points of interest - both technological and non-technological - to POC researchers and test developers. Technologically, we review design choices in assay chemistry, microfluidics, and instrumentation towards nucleic acid and protein detection for severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and away from the lab bench, developments that supported the unprecedented rapid development, scale up, and deployment of POC devices. We describe common features in the POC technologies that obtained Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for nucleic acid, antigen, and antibody tests, and how these tests fit into four distinct POC use cases. We conclude with implications for future pandemics, infectious disease monitoring, and digital health.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
Figures



References
-
- Sheridan C, Nat. Biotechnol, 2020, 38, 769–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

