Long-term evaluation of factors affecting removal torque of microimplants
- PMID: 34778924
- PMCID: PMC8590991
- DOI: 10.1186/s40510-021-00383-3
Long-term evaluation of factors affecting removal torque of microimplants
Abstract
Background: The current study aimed to evaluate factors affecting the long-term stability of microimplants using removal torque and the correlation between removal torque and clinical variables.
Materials and methods: This research evaluated 703 microimplants placed in 354 patients (mean age: 30.4 ± 12.1 years). The removal torque was evaluated according to various clinical variables including sex, age, placement site, microimplant size, and placement method (self-drilling versus pre-drilling). Pearson correlation and stepwise multiple linear regression analyses were performed to investigate different variables and their association with removal torque.
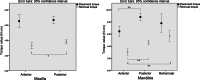
Results: The mean removal torque was significantly higher in the mandible (4.46 N cm) than in the maxilla (3.73 N cm). The values in the posterior teeth/retromolar areas were significantly higher than those in the anterior teeth area. There were no significant difference in terms of sex. Teenagers had a lower removal torque than older adults in the mandible, but not in the maxilla. Microimplants with a greater length and diameter, except for those with a greater diameter in the maxilla, was associated with a higher removal torque. Regardless of placement torque, the removal torque convergently reached approximately 4 N cm in both placement methods. The removal torque was significantly correlated with screw length in the self-drilling group and with diameter in the pre-drilling group.
Conclusions: Removal torque was related with placement site, age, placement method, and length and diameter of microimplants.
Keywords: Long-term stability; Microimplant; Placement method; Removal torque.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Influence of late removal after treatment on the removal torque of microimplants.Korean J Orthod. 2022 May 25;52(3):201-209. doi: 10.4041/kjod21.217. Korean J Orthod. 2022. PMID: 35418519 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical and histological comparison of self-drilling and self-tapping orthodontic microimplants in dogs.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008 Jan;133(1):44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.01.023. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008. PMID: 18174070
-
Factors affecting the long-term stability of orthodontic mini-implants.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010 May;137(5):588.e1-5; discussion 588-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2009.05.019. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010. PMID: 20451776
-
Placement and removal torque values of orthodontic miniscrew implants.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011 May;139(5):669-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2010.11.017. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011. PMID: 21536211
-
Effect of cortical bone thickness and implant placement torque on stability of orthodontic mini-implants.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007 Sep-Oct;22(5):779-84. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007. PMID: 17974113
References
-
- Antoszewska J, Papadopoulos MA, Park HS, Ludwig B. Five-year experience with orthodontic miniscrew implants: a retrospective investigation of factors influencing success rates. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136(2):158.e1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

