Organophosphorus pesticides exhibit compound specific effects in rat precision-cut lung slices (PCLS): mechanisms involved in airway response, cytotoxicity, inflammatory activation and antioxidative defense
- PMID: 34778934
- PMCID: PMC8748323
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-021-03186-x
Organophosphorus pesticides exhibit compound specific effects in rat precision-cut lung slices (PCLS): mechanisms involved in airway response, cytotoxicity, inflammatory activation and antioxidative defense
Abstract
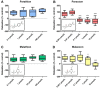
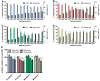
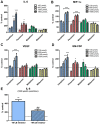
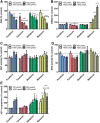
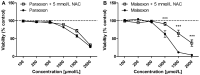
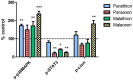
Organophosphorus compound pesticides (OP) are widely used in pest control and might be misused for terrorist attacks. Although acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition is the predominant toxic mechanism, OP may induce pneumonia and formation of lung edema after poisoning and during clinical treatment as life-threatening complication. To investigate the underlying mechanisms, rat precision-cut lung slices (PCLS) were exposed to the OP parathion, malathion and their biotransformation products paraoxon and malaoxon (100-2000 µmol/L). Airway response, metabolic activity, release of LDH, cytokine expression and oxidative stress response were analyzed. A concentration-dependent inhibition of airway relaxation was observed after exposure with the oxon but not with the thion-OP. In contrast, cytotoxic effects were observed for both forms in higher concentrations. Increased cytokine expression was observed after exposure to parathion and paraoxon (IL-6, GM-CSF, MIP-1α) and IL-6 expression was dependent on NFκB activation. Intracellular GSH levels were significantly reduced by all four tested OP but an increase in GSSG and HO-1 expression was predominantly observed after malaoxon exposure. Pretreatment with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine reduced malaoxon but not paraoxon-induced cytotoxicity. PCLS as a 3D lung model system revealed OP-induced effects depending on the particular OP. The experimental data of this study contribute to a better understanding of OP toxicity on cellular targets and may be a possible explanation for the variety of clinical outcomes induced by different OP.
Keywords: Bronchoconstriction; Inflammation; Organophosphates; Oxidative stress; PCLS.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Behrsing HP, Furniss MJ, Davis M, Tomaszewski JE, Parchment RE. In vitro exposure of precision-cut lung slices to 2-(4-amino-3-methylphenyl)-5-fluorobenzothiazole lysylamide dihydrochloride (NSC 710305, Phortress) increases inflammatory cytokine content and tissue damage. Toxicol Sci. 2013;131(2):470–479. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfs319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

