Adaptive homeostasis and the p53 isoform network
- PMID: 34779563
- PMCID: PMC8647153
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.202153085
Adaptive homeostasis and the p53 isoform network
Abstract
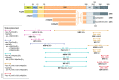
All living organisms have developed processes to sense and address environmental changes to maintain a stable internal state (homeostasis). When activated, the p53 tumour suppressor maintains cell and organ integrity and functions in response to homeostasis disruptors (stresses) such as infection, metabolic alterations and cellular damage. Thus, p53 plays a fundamental physiological role in maintaining organismal homeostasis. The TP53 gene encodes a network of proteins (p53 isoforms) with similar and distinct biochemical functions. The p53 network carries out multiple biological activities enabling cooperation between individual cells required for long-term survival of multicellular organisms (animals) in response to an ever-changing environment caused by mutation, infection, metabolic alteration or damage. In this review, we suggest that the p53 network has evolved as an adaptive response to pathogen infections and other environmental selection pressures.
Keywords: homeostasis; immune response; inflammation; p53 isoforms; pathogen.
© 2021 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ali A, Farooqui SR, Rai J, Singh J, Kumar V, Mishra R, Banerjea AC (2020) HIV‐1 Nef promotes ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of p53 tumor suppressor protein by using E6AP. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 529: 1038–1044 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

