Childhood obesity: an ecological perspective
- PMID: 34780713
- PMCID: PMC9510906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jped.2021.10.002
Childhood obesity: an ecological perspective
Abstract
Objective: To describe the participation of the environment in the childhood obesity epidemic, since childhood obesity currently represents a great challenge, with high prevalence worldwide, including in Brazil.
Data source: Survey of articles published in the last 10 years in PubMed, evaluating the interface between the environment and childhood obesity.
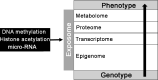
Data synthesis: Recent studies show that the environment is very important in the etiopathogenesis of obesity and its comorbidities. Therefore, factors such as air pollution, exposure to chemical substances that interfere with the metabolism, excessive consumption of ultra-processed foods, changes in the intestinal microbiota, and sedentary lifestyle are associated with increased obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and changes in lipid metabolism. These factors have a greater impact on some stages of life, such as the first thousand days, as they affect the expression of genes that control the adipogenesis, energy expenditure, and the mechanisms for hunger/satiety control.
Conclusions: Environmental aspects must be taken into account in the prevention and treatment of childhood obesity, both from the individual and the population point of view, with adequate and comprehensive public health policies.
Keywords: Childhood obesity; Endocrine disruptors; Epigenetics; Microbiota; Sedentary lifestyle; Ultra-processed food.
Copyright © 2021 Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Obesity Federation. Atlas of childhood obesity. [cited 2021 Jul 31]. Available from:ttps://data.worldobesity.org/publications/11996-Childhood-Obesity-Atlas-...
-
- Jia P. Obesogenic environment and childhood obesity. Obes Rev. 2021;22(S1):e13158. - PubMed
-
- Luo Y.N., Huang W.Z., Liu X.X., Markevych I., Bloom M.S., Zhao T., et al. Greenspace with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies up to 2020. Obes Rev. 2020;21:e13078. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical