Quality of life in patients with diabetic nephropathy: findings from the KNOW-CKD (Korean Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease) cohort
- PMID: 34781641
- PMCID: PMC8816412
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.21.068
Quality of life in patients with diabetic nephropathy: findings from the KNOW-CKD (Korean Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease) cohort
Abstract
Background: Diabetic nephropathy (DN) can affect quality of life (QoL) because it requires arduous lifelong management. This study analyzed QoL differences between DN patients and patients with other chronic kidney diseases (CKDs).
Methods: The analysis included subjects (n = 1,766) from the KNOW-CKD (Korean Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease) cohort who completed the Kidney Disease Quality of Life Short Form questionnaire. After implementing propensity score matching (PSM) using factors that affect the QoL of DN patients, QoL differences between DN and non-DN participants were examined.
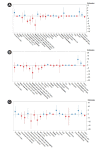
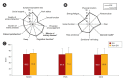
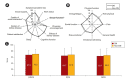
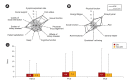
Results: Among all DN patients (n = 390), higher QoL scores were found for taller subjects, and lower scores were found for those who were unemployed or unmarried, received Medical Aid, had lower economic status, had higher platelet counts or alkaline phosphatase levels, or used clopidogrel or insulin. After PSM, the 239 matched DN subjects reported significantly lower patient satisfaction (59.9 vs. 64.5, p = 0.02) and general health (35.3 vs. 39.1, p = 0.04) than the 239 non-DN subjects. Scores decreased in both groups during the 5-year follow-up, and the scores in the work status, sexual function, and role-physical domains were lower among DN patients than non-DN patients, though those differences were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Socioeconomic factors of DN were strong risk factors for impaired QoL, as were high platelet, alkaline phosphatase, and clopidogrel and insulin use. Clinicians should keep in mind that the QoL of DN patients might decrease in some domains compared with non-DN CKDs.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy; Kidney Disease Quality of Life Short Form questionnaire; Kidney disease component summary; Mental component summary; Physical component summary; Quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The development and validation of the Norfolk QOL-DN, a new measure of patients' perception of the effects of diabetes and diabetic neuropathy.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2005 Jun;7(3):497-508. doi: 10.1089/dia.2005.7.497. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15929681
-
The Cost and Quality of Life of Malaysian Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Anemia.Value Health Reg Issues. 2018 May;15:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Value Health Reg Issues. 2018. PMID: 29474177
-
Health-Related Quality of Life of Kidney Transplantation Patients: Results from the KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcome in Patients With Kidney Transplantation (KNOW-KT) Study.Transplant Proc. 2016 Apr;48(3):844-7. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.12.101. Transplant Proc. 2016. PMID: 27234749
-
Physical component quality of life reflects the impact of time and moderate chronic kidney disease, unlike SF-6D utility and mental component SF-36 quality of life: An AusDiab analysis.Nephrology (Carlton). 2019 Jun;24(6):605-614. doi: 10.1111/nep.13445. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Nephrology (Carlton). 2019. PMID: 30039893
-
Diabetic nephropathy: recent advances in pathophysiology and challenges in dietary management.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019 Jan 23;11:7. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0403-4. eCollection 2019. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 30679960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Socioeconomic inequality in health-related quality of life among Korean adults with chronic disease: an analysis of the Korean Community Health Survey.Epidemiol Health. 2024;46:e2024018. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2024018. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Epidemiol Health. 2024. PMID: 38228085 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the rationale and conducting a comprehensive assessment of AdipoRon (adiponectin receptor agonist) as a candidate drug for diabetic nephropathy and cardiomyopathy prevention and intervention-a systematic review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;398(1):165-177. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03362-7. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39136737
References
-
- Hays RD, Kallich JD, Mapes DL, et al. Kidney Disease Quality of Life Short Form (KDQOL-SF), version 1.3: a manual for use and scoring. Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corp.; 1997. p. 39.
-
- Bradley C, Speight J. Patient perceptions of diabetes and diabetes therapy: assessing quality of life. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002;18 Suppl 3:S64–S69. - PubMed
-
- Cox D, Gonder-Frederick L, McCall A, Kovatchev B, Clarke W. The effects of glucose fluctuation on cognitive function and QOL: the functional costs of hypoglycaemia and hyperglycaemia among adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2002:20–26. - PubMed
-
- Undén AL, Elofsson S, Andréasson A, Hillered E, Eriksson I, Brismar K. Gender differences in self-rated health, quality of life, quality of care, and metabolic control in patients with diabetes. Gend Med. 2008;5:162–180. - PubMed
-
- Akinci F, Yildirim A, Gözü H, Sargin H, Orbay E, Sargin M. Assessment of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of patients with type 2 diabetes in Turkey. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;79:117–123. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2011E3300300/Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- 2012E3301100/Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- 2013E3301600/Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- 2013E3301601/Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- 2013E3301602/Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

