Working to Increase Stability through Exercise (WISE): screening, recruitment, and baseline characteristics
- PMID: 34781994
- PMCID: PMC8591922
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-021-05761-0
Working to Increase Stability through Exercise (WISE): screening, recruitment, and baseline characteristics
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Working to increase stability through exercise (WISE): screening, recruitment, and baseline characteristics.Trials. 2022 Jan 14;23(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06018-0. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35031069 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
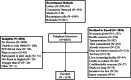
Background: The aim of this paper is to describe the utility of various recruitment modalities utilized in the Working to Increase Stability through Exercise (WISE) study. WISE is a pragmatic randomized trial that is testing the impact of a 3-year, multicomponent (strength, balance, aerobic) physical activity program led by trained volunteers or delivered via DVD on the rate of serious fall-related injuries among adults 65 and older with a past history of fragility fractures (e.g., vertebral, fall-related). The modified goal was to recruit 1130 participants over 2 years in three regions of Pennsylvania.
Methods: The at-risk population was identified primarily using letters mailed to patients of three health systems and those over 65 in each region, as well as using provider alerts in the health record, proactive recruitment phone calls, radio advertisements, and presentations at community meetings.
Results: Over 24 months of recruitment, 209,301 recruitment letters were mailed, resulting in 6818 telephone interviews. The two most productive recruitment methods were letters (72% of randomized participants) and the research registries at the University of Pittsburgh (11%). An average of 211 letters were required to be mailed for each participant enrolled. Of those interviewed, 2854 were ineligible, 2,825 declined to enroll and 1139 were enrolled and randomized. Most participants were female (84.4%), under age 75 (64.2%), and 50% took an osteoporosis medication. Not having a prior fragility fracture was the most common reason for not being eligible (87.5%). The most common reason provided for declining enrollment was not feeling healthy enough to participate (12.6%).
Conclusions: The WISE study achieved its overall recruitment goal. Bulk mailing was the most productive method for recruiting community-dwelling older adults at risk of serious fall-related injury into this long-term physical activity intervention trial, and electronic registries are important sources and should be considered.
Keywords: Exercise; Fall-related; Falls; Osteoporosis; Physical activity.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Sciamanna is part-owner of BandUp, Inc., formed to test the viability of various strategies to disseminate the WISE study findings. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kramarow E, Chen LH, Hedegaard H, Warner M. Deaths from unintentional injury among adults aged 65 and over: United States, 2000-2013. NCHS Data Brief. 2015;199:199. - PubMed
-
- Ortman JM, Velkoff VA, Hogan H. An Aging Nation: The Older Population in the United States. U.S. Census Bureau: Washington, D.C; 2014.
-
- Sciamanna C, Ballentine NH, Bopp M, Brach JS, Chinchilli VM, Ciccolo JT, Conroy MB, Fisher A, Fox EJ, Greenspan SL, Jan de Beur, Suzanne M, Kearcher K, Kraschnewski JL, McTigue KM, McAuley E, Morone NE, Paranjape A, Rodriguez-Colon S, Rosenzweig A, Smyth JM, Stewart KJ, Stuckey HL. Working to Increase Stability through Exercise (WISE): Study protocol for a pragmatic randomized controlled trial of a coached exercise program to reduce serious fall-related injuries. Contemp Clin Trials. 2018;74:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2018.09.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous