Development of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Distress Scale (RADS): a new tool to identify disease-specific distress in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 34782021
- PMCID: PMC8594165
- DOI: 10.1186/s41927-021-00220-4
Development of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Distress Scale (RADS): a new tool to identify disease-specific distress in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Background: Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) may experience psychological distress (depression, anxiety) in addition to their physical symptoms. People with RA may also experience disease-specific distress (DSD), related to the specific burden of living with their life-long condition. DSD is a patient reported outcome in several long-term conditions, including type 1 and 2 diabetes. The aims of this study were to determine whether DSD is experienced by people with RA, and if so, develop a Patient Reported Outcome Measure (PROM) to assess for DSD in people with RA.
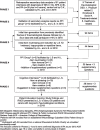
Methods: A five-phased qualitative study was conducted which consisted of a secondary data analysis of 61 interviews of people with rheumatological disease (Phase 1), validation of findings via a Patient and Public Involvement (PPI) group of people with RA (n = 4) (Phase 2), item generation for a PROM (Phase 3) and establishing face and content validity of the PROM via PPI group (n = 4) and individual cognitive interviews (n = 9) of people with RA respectively (Phase 4 and 5). The final PROM was presented at a Patient Education Evening for patients with long-term rheumatological conditions, including RA, and carers.
Results: Five themes of rheumatological disease distress emerged from Phase 1, which were validated in the Phase 2 PPI group. After Phases 3-5, the Rheumatoid Arthritis Distress Scale (RADS) was formed of 39 items and 3 supplementary questions. Overall participants reported the content of the RADS to be clear and relevant, and that DSD is a valid concept in RA, distinct from other entities like clinical depression or anxiety.
Conclusions: DSD appears to be an important concept in RA. The 39-item RADS demonstrates acceptable face and content validity in this patient group. Further psychometric testing is needed. The RADS may be a useful tool for healthcare professionals to identify RA distress.
Keywords: Distress; Patient Reported Outcome Measure; Qualitative research; Rheumatoid Arthritis; Secondary analysis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JS received royalties from the University of Warwick in relation to the Diabetes Manual programme. There are no conflicts of interest for all other authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development, psychometric evaluation and cognitive debriefing of the rheumatoid arthritis symptom and impact questionnaire (RASIQ).J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2021 Dec 11;5(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s41687-021-00400-3. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2021. PMID: 34894330 Free PMC article.
-
Development and application of a questionnaire to assess patient beliefs in rheumatoid arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Oct;37(10):2649-2657. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4172-5. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29948351 Free PMC article.
-
Development and testing of candidate items for inclusion in a new rheumatoid arthritis stiffness patient-reported outcome measure.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018 Feb 1;57(2):263-272. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex085. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018. PMID: 28407140
-
Telephone interventions for symptom management in adults with cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jun 2;6(6):CD007568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007568.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32483832 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological well-being in rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the literature.Musculoskeletal Care. 2010 Jun;8(2):99-106. doi: 10.1002/msc.171. Musculoskeletal Care. 2010. PMID: 20232479 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a novel clinimetric tool: PAtient Reported Disease Activity Index in Rheumatoid Arthritis (PARDAI-RA) by PANLAR, for the assessment of patients living with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Apr;43(4):1277-1285. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06868-w. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38355831 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of refractory disease and persistent symptoms in inflammatory arthritis: Qualitative framework analysis of interviews with patients and health care professionals.Br J Health Psychol. 2025 Feb;30(1):e12780. doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12780. Br J Health Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39777948 Free PMC article.
-
Refractory inflammatory arthritis definition and model generated through patient and multi-disciplinary professional modified Delphi process.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 9;18(8):e0289760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289760. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37556424 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical