Transgenic rice plants expressing the α-L-arabinofuranosidase of Coprinopsis cinerea exhibit strong dwarfism and markedly enhanced tillering
- PMID: 34782826
- PMCID: PMC8562574
- DOI: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.21.0616a
Transgenic rice plants expressing the α-L-arabinofuranosidase of Coprinopsis cinerea exhibit strong dwarfism and markedly enhanced tillering
Abstract
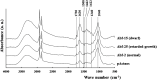
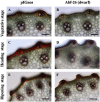
Lignocellulosic materials are potential renewable sources of fermentable sugars for bioethanol production. In this study, we used the CcAbf62A gene encoding CcAbf62A, a putative extracellular α-L-arabinofuranosidase, cloned from the mycotrophic basidiomycete Coprinopsis cinerea. CcAbf62A acts on arabinoxylan, the major hemicellulose of grasses, releasing arabinose. CcAbf62A was introduced into rice with the aim of enhancing delignification efficiency and the availability of lignocellulosic materials without reducing lignin content. Among the 32 lines of regenerated transgenic rice, 13 exhibited markedly disrupted elongation growth and excessive tillering (dwarf), seven showed delayed elongation growth (retarded-growth), and 12 showed phenotypes similar to those of control plants (normal). Additionally, the dwarf lines showed reduced acclimation. RT-PCR analysis revealed that dwarf lines had higher levels of CcAbf62A expression than retarded-growth and normal lines. Although the lignin content of transgenic rice plants expressing CcAbf62A did not differ significantly from that of control rice plants, dwarf lines were characterized by delayed deposition of lignin in the culms compared with the controls. The reduced acclimation ability of dwarf lines is believed to be associated with increased water loss and reduced water conductivity concomitant with delayed lignin deposition. Contrary to expectations, the alkaline delignification rates of dwarf and retarded-growth Abf lines were slightly lower than those of control rice plants. Our findings indicate that CcAbf62A reduces ferulate-lignin cross-links by detaching arabinose side chains from arabinoxylan and increases the relative abundance of alkaline-resistant benzyl ether cross-links. CcAbf62A is anticipated to provide new approaches for breeding plants containing altered lignocellulosic materials or lodging-resistant crops.
Keywords: Coprinopsis cinerea; arabinofuranosidase; delignification; dwarfism; lignocellulosic material.
© 2021 Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of CcAbf62A, a GH62 α-L-arabinofuranosidase, from the basidiomycete Coprinopsis cinerea.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(2):342-5. doi: 10.1271/bbb.100434. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21307589
-
Structure of the Catalytic Domain of α-L-Arabinofuranosidase from Coprinopsis cinerea, CcAbf62A, Provides Insights into Structure-Function Relationships in Glycoside Hydrolase Family 62.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2017 Feb;181(2):511-525. doi: 10.1007/s12010-016-2227-0. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27589854
-
Downregulation of a UDP-Arabinomutase Gene in Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) Results in Increased Cell Wall Lignin While Reducing Arabinose-Glycans.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Oct 27;7:1580. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01580. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27833622 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of key pretreatment processes for biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol.3 Biotech. 2015 Oct;5(5):597-609. doi: 10.1007/s13205-015-0279-4. Epub 2015 Feb 3. 3 Biotech. 2015. PMID: 28324530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging strategies of lignin engineering and degradation for cellulosic biofuel production.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2008 Apr;19(2):166-72. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2008.02.014. Epub 2008 Apr 9. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18403196 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of regulatory mechanisms associated with uniconazole-induced dwarfism in banana.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Dec 28;22(1):614. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-04005-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36575388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akama K, Shiraishi H, Ohta S, Nakamura K, Okada K, Shimura Y (1992) Efficient transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana: Comparison of the efficiencies with various organs, plant ecotypes and Agrobacterium strains. Plant Cell Rep 12: 7–11 - PubMed
-
- Buanafina MM de O, Langdon T, Hauck B, Dalton S, Morris P (2008) Expression of a fungal ferulic acid esterase increases cell wall digestibility of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea). Plant Biotechnol J 6: 264–280 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
