Regulation of PCSK9 Expression and Function: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 34782856
- PMCID: PMC8589637
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.764038
Regulation of PCSK9 Expression and Function: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
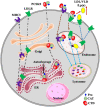
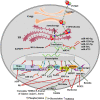
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) promotes degradation of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and plays a central role in regulating plasma levels of LDL cholesterol levels, lipoprotein(a) and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, PCSK9 promotes degradation of major histocompatibility protein class I and reduces intratumoral infiltration of cytotoxic T cells. Inhibition of PCSK9 increases expression of LDLR, thereby reducing plasma levels of lipoproteins and the risk of cardiovascular disease. PCSK9 inhibition also increases cell surface levels of major histocompatibility protein class I in cancer cells and suppresses tumor growth. Therefore, PCSK9 plays a vital role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and cancer, the top two causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Monoclonal anti-PCSK9 antibody-based therapy is currently the only available treatment that can effectively reduce plasma LDL-C levels and suppress tumor growth. However, high expenses limit their widespread use. PCSK9 promotes lysosomal degradation of its substrates, but the detailed molecular mechanism by which PCSK9 promotes degradation of its substrates is not completely understood, impeding the development of more cost-effective alternative strategies to inhibit PCSK9. Here, we review our current understanding of PCSK9 and focus on the regulation of its expression and functions.
Keywords: LDL receptor; PCSK9; atherosclerosis; cancer immunotherapy; cardiovascular disease; lipid metabolism; major histocompatibility protein class I.
Copyright © 2021 Xia, Peng, Gu, Wang, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

