Taiwan accelerates its efforts to eliminate hepatitis C
- PMID: 34782872
- PMCID: PMC8562095
- DOI: 10.35772/ghm.2021.01064
Taiwan accelerates its efforts to eliminate hepatitis C
Abstract
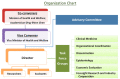
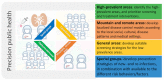
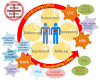
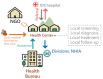
The estimated prevalence of anti-HCV was 3.3% (1.8-5.5%) in the general population in Taiwan with several regional disparities. The reactive anti-HCV in different regions may vary between 0% and 65%. The National Hepatitis C Program (NHCP) office estimated approximately 623,323 persons reactive with anti-HCV based on several extensive region- and cohort-wide studies. Taiwan has accelerated its efforts to eliminate hepatitis C since 2018 by committing to achieve World Health Organization (WHO)'s 2030 goal of treating 80% of eligible patients by 2025. Many aggressive measures by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) have been ongoing including several key success factors such as political commitment by the MOHW to finance this national program and improve National Health Insurance (NHI) reimbursement restrictions for treatment. Meanwhile, the Taiwan Centers for Disease Control (CDC) instituted harm reduction programs and the Health Promotion Administration (HPA) started to improve awareness and perform national screening programs. The NHCP office instituted monitoring, evaluation, micro-elimination and funding to linkage to care programs. In addition to sustainable financing, it is imperative to scale-up screening coverage through a precision public health approach to fill the gap of under-diagnosis. Hopefully, we can achieve early elimination by announcing the treatment target of 250000 CHC patients by 2025.
Keywords: HCV elimination; National Hepatitis C Program; Taiwan's effort.
2021, National Center for Global Health and Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Global report on access to hepatitis C treatment: focus on overcoming barriers. Geneva. 2016. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/global-report-on-access-to-hepat... (accessed on June 1, 2021).
-
- Bennett H, Waser N, Johnston K, Kao JH, Lim YS, Duan ZP, Lee YJ, Wei L, Chen CJ, Sievert W, Yuan Y, Li H. A review of the burden of hepatitis C infection in China, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan. Hepatol Int. 2015; 9:378-390. - PubMed
-
- Polaris Observatory HCV Collaborators. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 2:161-176. - PubMed
-
- Wu GH, Pwu RF, Chen SC, Chen DS. Taiwan is on track of accelerating hepatitis C elimination by 2025. Liver Int. 2020; 40:1506-1507. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

