Maternal Plasma and Amniotic Fluid LBP, Pentraxin 3, Resistin, and IGFBP-3: Biomarkers of Microbial Invasion of Amniotic Cavity and/or Intra-amniotic Inflammation in Women with Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes
- PMID: 34783213
- PMCID: PMC8593411
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e279
Maternal Plasma and Amniotic Fluid LBP, Pentraxin 3, Resistin, and IGFBP-3: Biomarkers of Microbial Invasion of Amniotic Cavity and/or Intra-amniotic Inflammation in Women with Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes
Abstract
Background: We sought to determine whether lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP), pentraxin 3, resistin, and insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 in plasma and amniotic fluid (AF) can predict microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity (MIAC), intra-amniotic inflammation (IAI), and microbial-associated IAI in women with preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM).
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study involving 168 singleton pregnant women with PPROM. AF obtained via amniocentesis was cultured and assayed for interleukin (IL)-6 to define IAI and for IL-8 to compare with AF biomarkers. Plasma samples were collected at the time of amniocentesis, and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in serum were compared with plasma biomarkers. The stored plasma and AF samples were assayed for LBP, pentraxin 3 (PTX3), resistin, and IGFBP-3 by ELISA.
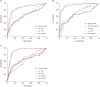
Results: Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that: 1) elevated plasma and AF levels of LBP were independently associated with increased risks of MIAC, IAI, and microbial-associated IAI; 2) elevated AF, but not plasma, PTX3, and resistin levels were independently associated with increased risks of MIAC, IAI, and microbial-associated IAI; 3) decreased IGFBP-3 levels in the plasma were independently associated with only IAI, whereas those in the AF were associated with only microbial-associated IAI. Among the tested biomarkers, AF PTX3 and resistin had the highest predictive performance for MIAC, IAI, and microbial-associated IAI (area under the curves [AUC] = 0.85-0.95), which is similar to the performance of AF IL-8. The AUCs of the plasma LBP and IGFBP-3 were similar to that of serum CRP with respect to IAI.
Conclusion: Maternal plasma LBP and IGFBP-3 are potential biomarkers for the non-invasive identification of IAI in women with PPROM, with a similar accuracy to the serum CRP level. AF LBP, PTX3, resistin, and IGFBP-3 may be involved in the intra-amniotic inflammatory responses in PPROM complicated by MIAC.
Keywords: Amniotic Fluid; IGFBP-3; Inflammatory Mediators; Intra-Amniotic Inflammation; Microbial Invasion of Amniotic Cavity; Plasma; Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes.
© 2021 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

