Tumor-associated macrophages in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 34783219
- PMCID: PMC8593527
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B2100029
Tumor-associated macrophages in osteosarcoma
Abstract
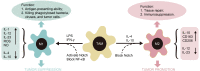
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary bone tumor in children and adolescents. It is an aggressive tumor with a tendency to spread to the lung, which is the most common site of metastasis. Patients with advanced OS with metastases have poor prognoses despite the application of chemotherapy, thus highlighting the need for novel therapeutic targets. The tumor microenvironment (TME) of OS is confirmed to be essential for and supportive of tumor growth and dissemination. The immune component of the OS microenvironment is mainly composed of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). In OS, TAMs promote tumor growth and angiogenesis and upregulate the cancer stem cell-like phenotype. However, TAMs inhibit the metastasis of OS. Therefore, much attention has been paid to investigating the mechanism of TAMs in OS development and the progression of immunotherapy for OS. In this article, we aim to summarize the roles of TAMs in OS and the major findings on the application of TAMs in OS treatment.
Keywords: Osteosarcoma; Tumor microenvironment; Tumor-associated macrophage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of tumor-associated macrophages in osteosarcoma progression - therapeutic implications.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Jun;44(3):525-539. doi: 10.1007/s13402-021-00598-w. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 33788151 Review.
-
Osteosarcoma cell-derived CCL2 facilitates lung metastasis via accumulation of tumor-associated macrophages.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025 May 9;74(7):193. doi: 10.1007/s00262-025-04051-x. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40343498 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Osteosarcoma: From Mechanisms to Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 23;21(15):5207. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155207. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32717819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the effects of M2 macrophage-derived PDE4C on the prognosis, metastasis and immunotherapy benefit of osteosarcoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(10):e18395. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18395. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38774995 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal role of IL-8 derived from the interaction between osteosarcoma and tumor-associated macrophages in osteosarcoma growth and metastasis via the FAK pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 1;15(2):108. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06487-y. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38302407 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Regulating the Plasticity of Osteosarcoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 18;23(24):16155. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416155. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical characterization of a new sulfated polysaccharide from Gracilaria chouae and its activation effects on RAW264.7 macrophages.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Jan 15;23(1):84-88. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2100508. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 35029090 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs: typical biomarkers for bone-related diseases.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Dec 15;23(12):975-988. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2200211. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 36518051 Free PMC article.
-
Make it STING: nanotechnological approaches for activating cGAS/STING as an immunomodulatory node in osteosarcoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 30;15:1403538. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1403538. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39403376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SPON2 facilitates osteosarcoma development by inducing M2 macrophage polarization through activation of the NF-κB/VEGF signaling axis.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jul 29;11(1):352. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02626-2. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40730813 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

