Fast alignment of reads to a variation graph with application to SNP detection
- PMID: 34783230
- PMCID: PMC8709736
- DOI: 10.1515/jib-2021-0032
Fast alignment of reads to a variation graph with application to SNP detection
Abstract
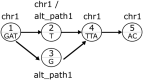
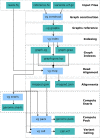
Sequencing technologies has provided the basis of most modern genome sequencing studies due to its high base-level accuracy and relatively low cost. One of the most demanding step is mapping reads to the human reference genome. The reliance on a single reference human genome could introduce substantial biases in downstream analyses. Pangenomic graph reference representations offer an attractive approach for storing genetic variations. Moreover, it is possible to include known variants in the reference in order to make read mapping, variant calling, and genotyping variant-aware. Only recently a framework for variation graphs, vg [Garrison E, Adam MN, Siren J, et al. Variation graph toolkit improves read mapping by representing genetic variation in the reference. Nat Biotechnol 2018;36:875-9], have improved variation-aware alignment and variant calling in general. The major bottleneck of vg is its high cost of reads mapping to a variation graph. In this paper we study the problem of SNP calling on a variation graph and we present a fast reads alignment tool, named VG SNP-Aware. VG SNP-Aware is able align reads exactly to a variation graph and detect SNPs based on these aligned reads. The results show that VG SNP-Aware can efficiently map reads to a variation graph with a speedup of 40× with respect to vg and similar accuracy on SNPs detection.
Keywords: SNP detection; reads alignment; variation graph.
© 2021 Maurilio Monsu and Matteo Comin published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Figures
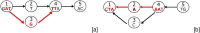
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
