Safety levels of systemic IL-12 induced by cDNA expression as a cancer therapeutic
- PMID: 34783257
- PMCID: PMC8739399
- DOI: 10.2217/imt-2021-0080
Safety levels of systemic IL-12 induced by cDNA expression as a cancer therapeutic
Abstract
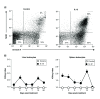
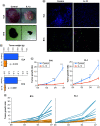
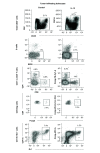
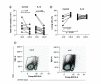
Aim: The aim of this work is to utilize a gene expression procedure to safely express systemic IL-12 and evaluate its effects in mouse tumor models. Materials & methods: Secondary lymphoid organs and tumors from EL4 and B16 tumor-bearing mice were analyzed by supervised and unsupervised methods. Results: IL-12 cDNA induced systemic IL-12 protein levels lower than the tolerated dose in patients. Control of tumor growth was observed in subcutaneous B16 and EL4 tumors. Systemic IL-12 expression induced a higher frequency of both total tumor-infiltrated CD45+ cells and proliferative IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells along with a lower frequency of CD4+FOXP3+ and CD11b+Gr-1+ cells. Conclusion: This approach characterizes the systemic effects of IL-12, helping to improve treatment of metastases or solid tumors.
Keywords: B16; CD8+ T cells; EL4; IFN-γ; cancer; hydrodynamic injection; immunotherapy; secondary lymphoid organs; systemic IL-12; tumor microenvironment.
Plain language summary
Lay abstract IL-12 has emerged as a potent cytokine in mediating antitumor activity in preclinical models of cancer. However, this antitumor response has not yet been translated into the clinic because of toxic side effects. The aim of our work is to analyze the effects of IL-12 in mouse tumor models. We demonstrate that one injection of IL-12 cDNA can induce systemic IL-12 levels in serum even lower than the tolerated dose in patients. At this dose, an efficient control of tumor growth can be observed. We found a higher frequency of both total tumor-infiltrated leukocytes and IFN-γ-producing CD8+ T cells along with a lower frequency of regulatory CD4+FOXP3+ and CD11b+Gr1+ cells. Our work demonstrates that IL-12 cDNA can safely be used to treat cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
This project has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds directly from the intramural research programs of the National Cancer Institute, CCR, LCIM under Contract no. HHSN261200800001E. Fundación para el Progreso de la Medicina GC N°1, Secretaria de Ciencia y Tecnología de la UNC (SeCyT-UNC). This project has been funded in part with federal funds from the Intramural Research Program of the Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute (NCI): ZIA BC 009283. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Abrogation of TNFα production during cancer immunotherapy is crucial for suppressing side effects due to the systemic expression of IL-12.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e90116. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090116. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587231 Free PMC article.
-
Coexpression of IL-18 strongly attenuates IL-12-induced systemic toxicity through a rapid induction of IL-10 without affecting its antitumor capacity.J Immunol. 2009 Jul 1;183(1):740-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804166. Epub 2009 Jun 17. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19535628 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-33 pretreatment promotes metastatic growth of murine melanoma by reducing the cytotoxic capacity of CD8+ T cells and enhancing regulatory T cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020 Aug;69(8):1461-1475. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02522-x. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32285171 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a tumor-specific systemic response after intratumoral injection of IL-12 and IL-18-loaded polylactic acid microspheres.J Immunother. 2007 Nov-Dec;30(8):808-16. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e318156e6a7. J Immunother. 2007. PMID: 18049332
-
Significant antitumor effects obtained by autologous tumor cell vaccine engineered to secrete interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18 by means of the EBV/lipoplex.Mol Ther. 2002 May;5(5 Pt 1):609-16. doi: 10.1006/mthe.2002.0587. Mol Ther. 2002. PMID: 11991752
Cited by
-
Systemic inflammatory Th1 cytokines during Trypanosoma cruzi infection disrupt the typical anatomical cell distribution and phenotypic/functional characteristics of various cell subsets within the thymus.Microbes Infect. 2024 Jul-Aug;26(5-6):105337. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2024.105337. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38615883 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the immunomodulatory role of virtual memory CD8+ T cells: Role of IFN gamma in tumor growth control.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 18;13:971001. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.971001. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36330506 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Activities of Interleukin-12 in Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 14;14(22):5592. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225592. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428682 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
