LINC01232 serves as a novel biomarker and promotes tumour progression by sponging miR-204-5p and upregulating RAB22A in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34783622
- PMCID: PMC8604453
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2021.2001563
LINC01232 serves as a novel biomarker and promotes tumour progression by sponging miR-204-5p and upregulating RAB22A in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in the progression of various cancers, including clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). This study aimed to investigate the expression and prognostic value of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA (LINC) 01232 in ccRCC and preliminary explore the molecular mechanism underlying the role of LINC01232 in ccRCC progression.
Methods: Tumour tissues and adjacent normal tissues of 122 patients with ccRCC were collected in this study. The levels of LINC01232, microRNA (miR)-204-5p and RAB22A were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. The proliferation, migration and invasion of ccRCC cells were detected by cell counting kit-8 assay and Transwell assay, respectively. The interaction among LINC01232, miR-204-5p and RAB22A was confirmed by bioinformatics analysis, dual-luciferase reporter assay and Pearson correlation analysis. The association of LINC01232 and miR-204-5p with ccRCC patient survival was verified by the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. The prognostic value of LINC01232 in ccRCC was confirmed by Cox regression analysis.
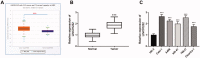
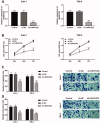
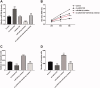
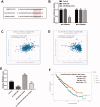
Results: LINC01232 expression was increased in ccRCC tumour tissues and ccRCC cells and independently predicted the prognosis of ccRCC patients. In addition, LINC01232 silencing inhibited ccRCC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Moreover, LINC01232 served as a sponge for miR-204-5p, and miR-204-5p reduction reversed the inhibitory effect of LINC01232 silencing on ccRCC cell function. Furthermore, LINC01232 could sponge miR-204-5p, causing the elevation of RAB22A in ccRCC, thereby promoting ccRCC cell function.
Conclusion: LINC01232 may be an independent prognostic biomarker in ccRCC and plays an oncogenic role in ccRCC progression by sponging miR-204-5p and upregulating RAB22A.
Keywords: LINC01232; RAB22A; clear cell renal cell carcinoma; miR-204-5p; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Linc00239 Facilitates the Progress of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma via the miR-204-5p/RAB22A Axis.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;67(6):2357-2366. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01202-w. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38850457 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via targeting miR-10a/SKA1 pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Mar;111:917-925. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.143. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30841471
-
CircPVT1 promotes progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by sponging miR-145-5p and regulating TBX15 expression.Cancer Sci. 2021 Apr;112(4):1443-1456. doi: 10.1111/cas.14814. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33453148 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding frontiers in liquid biopsy-discovery and validation of circulating biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma and bladder cancer.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2025;391:135-197. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2024.08.005. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39939075 Review.
-
Exploring necrosis-associated mitochondrial gene signatures: revealing their role in prognosis and immunotherapy of renal clear cell carcinoma.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jul 18;24(1):161. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01426-9. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39023752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A review on the role of long non-coding RNA and microRNA network in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its tumor microenvironment.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Feb 2;23(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02861-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 36732762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of prognostic value and immunological roles of RAB22A in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 3;14:1086342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1086342. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36936971 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal lncRNA LINC02191 Promotes Laryngeal Squamous cell Carcinoma Progression by Targeting miR-204-5p/RAB22A Axis and Regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway.Biochem Genet. 2024 Jun;62(3):2117-2133. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10541-3. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37863866
-
Variable roles of miRNA- and apoptosis-linked genes in invasive breast cancer: expression patterns, clinicopathological associations, and prognostic significance.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 11;52(1):703. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10739-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40643805
-
Cuproptosis-Associated lncRNA Establishes New Prognostic Profile and Predicts Immunotherapy Response in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 15;13:938259. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.938259. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35910212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M, et al. . Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(5):706–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
