Functional foods as a formulation ingredients in beverages: technological advancements and constraints
- PMID: 34783642
- PMCID: PMC8810194
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2005992
Functional foods as a formulation ingredients in beverages: technological advancements and constraints
Abstract
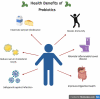
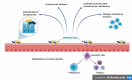
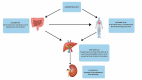
As a consequence of expanded science and technical research, the market perception of consumers has shifted from standard traditional to valuable foods, which are furthermore nutritional as well as healthier in today's world. This food concept, precisely referred to as functional, focuses on including probiotics, which enhance immune system activity, cognitive response, and overall health. This review primarily focuses on functional foods as functional additives in beverages and other food items that can regulate the human immune system and avert any possibility of contracting the infection. Many safety concerns must be resolved during their administration. Functional foods must have an adequate amount of specific probiotic strain(s) during their use and storage, as good viability is needed for optimum functionality of the probiotic. Thus, when developing novel functional food-based formulations, choosing a strain with strong technological properties is crucial. The present review focused on probiotics as an active ingredient in different beverage formulations and the exerting mechanism of action and fate of probiotics in the human body. Moreover, a comprehensive overview of the regulative and safety issues of probiotics-based foods and beverages formulations.
Keywords: Functional beverages; immune system; nutritional value; probiotic strain.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fermented cereal beverages: from probiotic, prebiotic and synbiotic towards Nanoscience designed healthy drinks.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017 Aug;65(2):114-124. doi: 10.1111/lam.12740. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28378421 Review.
-
Traditional low-alcoholic and non-alcoholic fermented beverages consumed in European countries: a neglected food group.Nutr Res Rev. 2017 Jun;30(1):1-24. doi: 10.1017/S0954422416000202. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Nutr Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28115036 Review.
-
Vegan probiotic products: A modern tendency or the newest challenge in functional foods.Food Res Int. 2021 Feb;140:110033. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.110033. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33648260 Review.
-
Probiotic properties of yeasts in traditional fermented foods and beverages.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 May;132(5):3533-3542. doi: 10.1111/jam.15467. Epub 2022 Feb 6. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35094453 Review.
-
Unveiling the potential of African fermented cereal-based beverages: Probiotics, functional drinks, health benefits and bioactive components.Food Res Int. 2024 Sep;191:114656. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114656. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39059934 Review.
Cited by
-
The Advent of Nutrigenomics: A Narrative Review with an Emphasis on Psychological Disorders.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2022 Jun 30;27(2):150-164. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2022.27.2.150. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 35919568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of gut bacteria on type 2 diabetes: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategy.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jan 15;16(1):100376. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i1.100376. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 39817222 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide candidates for the development of therapeutics and vaccines against β-coronavirus infection.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):9435-9454. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2060453. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35387556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of functional biscuits on intestinal mucosal microbiota composition, brain function, and antioxidant activity.Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2025;44(2):171-181. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.2024-078. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2025. PMID: 40171390 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Dysbiosis and Diabetic Foot Ulcer: Role of Probiotics.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 21;14(11):2543. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112543. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36432734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flach J, van der Waal MB, van Den Nieuwboer M, et al. The underexposed role of food matrices in probiotic products: reviewing the relationship between carrier matrices and product parameters. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018;58:2570–2584. - PubMed
-
- Annunziata A, Vecchio R.. Consumer perception of functional foods: a conjoint analysis with probiotics. Food Qual Prefer. 2013;28(1):348–355.
-
- Corbo MR, Bevilacqua A, Petruzzi L, et al. Functional beverages: the emerging side of functional foods: commercial trends, research, and health implications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2014;13(6):1192–1206.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
