Effect of intravenous cell therapy in rats with old myocardial infarction
- PMID: 34783963
- PMCID: PMC8896398
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-021-04283-2
Effect of intravenous cell therapy in rats with old myocardial infarction
Abstract
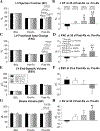
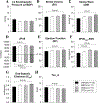
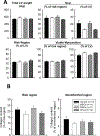
Mounting evidence shows that cell therapy provides therapeutic benefits in experimental and clinical settings of chronic heart failure. However, direct cardiac delivery of cells via transendocardial injection is logistically complex, expensive, entails risks, and is not amenable to multiple dosing. Intravenous administration would be a more convenient and clinically applicable route for cell therapy. Thus, we determined whether intravenous infusion of three widely used cell types improves left ventricular (LV) function and structure and compared their efficacy. Rats with a 30-day-old myocardial infarction (MI) received intravenous infusion of vehicle (PBS) or 1 of 3 types of cells: bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), cardiac mesenchymal cells (CMCs), and c-kit-positive cardiac cells (CPCs), at a dose of 12 × 106 cells. Rats were followed for 35 days after treatment to determine LV functional status by serial echocardiography and hemodynamic studies. Blood samples were collected for Hemavet analysis to determine inflammatory cell profile. LV ejection fraction (EF) dropped ≥ 20 points in all hearts at 30 days after MI and deteriorated further at 35-day follow-up in the vehicle-treated group. In contrast, deterioration of EF was halted in rats that received MSCs and attenuated in those that received CMCs or CPCs. None of the 3 types of cells significantly altered scar size, myocardial content of collagen or CD45-positive cells, or Hemavet profile. This study demonstrates that a single intravenous administration of 3 types of cells in rats with chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy is effective in attenuating the progressive deterioration in LV function. The extent of LV functional improvement was greatest with CPCs, intermediate with CMCs, and least with MSCs.
Keywords: Cell therapy; Fibrosis; Inflammation; Intravenous; Ischemic cardiomyopathy; Myocardial infarction; Repair; Stem cells.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

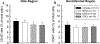
Similar articles
-
Intravenously Delivered Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects Improve Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Cardiomyopathy.Circ Res. 2017 May 12;120(10):1598-1613. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310599. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28232595
-
Repeated doses of cardiac mesenchymal cells are therapeutically superior to a single dose in mice with old myocardial infarction.Basic Res Cardiol. 2017 Mar;112(2):18. doi: 10.1007/s00395-017-0606-5. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Basic Res Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28210871 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells is safe for the lung in a chronic myocardial infarction model.Regen Med. 2011 Mar;6(2):179-90. doi: 10.2217/rme.10.104. Regen Med. 2011. PMID: 21391852
-
Comparison of Repeated Doses of C-kit-Positive Cardiac Cells versus a Single Equivalent Combined Dose in a Murine Model of Chronic Ischemic Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 19;22(6):3145. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063145. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808720 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan/silk fibroin modified nanofibrous patches with mesenchymal stem cells prevent heart remodeling post-myocardial infarction in rats.Acta Biomater. 2018 Oct 15;80:154-168. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.013. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30218777
Cited by
-
A new model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction induced by metabolic syndrome in Ossabaw miniature swine.Basic Res Cardiol. 2025 Jun;120(3):559-578. doi: 10.1007/s00395-025-01112-1. Epub 2025 May 1. Basic Res Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40312575 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Novel Effects in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 2;16:899887. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.899887. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35585925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone Marrow and Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells are Ineffective for Myocardial Repair in an Immunodeficient Rat Model of Chronic Ischemic Cardiomyopathy.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Oct;19(7):2429-2446. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10590-6. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 37500831 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic application of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction in myocardial infarction.iScience. 2024 Apr 18;27(5):109791. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109791. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38736548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current state of heart failure treatment: are mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes a future therapy?Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Apr 28;12:1518036. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1518036. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40357434 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hong KU, Guo Y, Li QH, Cao P, Al-Maqtari T, Vajravelu BN, Du J, Book MJ, Zhu X, Nong Y, Bhatnagar A, Bolli R (2014) c-kit+ Cardiac stem cells alleviate post-myocardial infarction left ventricular dysfunction despite poor engraftment and negligible retention in the recipient heart. PLoS ONE 9:e96725. 10.1371/journal.pone.0096725 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

