Trefoil Factor Family: A Troika for Lung Repair and Regeneration
- PMID: 34784491
- PMCID: PMC8937240
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0373TR
Trefoil Factor Family: A Troika for Lung Repair and Regeneration
Abstract
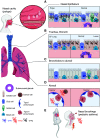
Tissue damage in the upper and lower airways caused by mechanical abrasion, noxious chemicals, or pathogenic organisms must be followed by rapid restorative processes; otherwise, persistent immunopathology and disease may ensue. This review will discuss evidence for the important role served by trefoil factor (TFF) family members in healthy and diseased airways of humans and rodents. Collectively, these peptides serve to both maintain and restore homeostasis through their regulation of the mucous layer and their control of cell motility, cell differentiation, and immune function in the upper and lower airways. We will also discuss important differences in which trefoil member tracks with homeostasis and disease between humans and mice, which poses a challenge for research in this area. Moreover, we discuss new evidence supporting newly identified receptor binding partners in the leucine-rich repeat and immunoglobulin-like domain-containing NoGo (LINGO) family in mediating the biological effects of TFF proteins in mouse models of epithelial repair and infection. Recent advances in our knowledge regarding TFF peptides suggest that they may be reasonable therapeutic targets in the treatment of upper and lower airway diseases of diverse etiologies. Further work understanding their role in airway homeostasis, repair, and inflammation will benefit from these newly uncovered receptor-ligand interactions.
Keywords: CXCR4; CXCR7; LINGO receptors; mucosal epithelium repair; trefoil factor family.
Figures


References
-
- Gilmour MI, Koren HS. In: Gehr P, Heyder J, editors. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 2000. Interaction of inhaled particles with the immune system; pp. 626–652.
-
- Thim L. A new family of growth factor-like peptides. ‘Trefoil’ disulphide loop structures as a common feature in breast cancer associated peptide (pS2), pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP), and frog skin peptides (spasmolysins) FEBS Lett . 1989;250:85–90. - PubMed
-
- Muskett FW, May FE, Westley BR, Feeney J. Solution structure of the disulfide-linked dimer of human intestinal trefoil factor (TFF3): the intermolecular orientation and interactions are markedly different from those of other dimeric trefoil proteins. Biochemistry . 2003;42:15139–15147. - PubMed
-
- Williams MA, Westley BR, May FE, Feeney J. The solution structure of the disulphide-linked homodimer of the human trefoil protein TFF1. FEBS Lett . 2001;493:70–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

