The influence of the site of drug administration on florfenicol pharmacokinetics in turkeys
- PMID: 34784513
- PMCID: PMC8591492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101536
The influence of the site of drug administration on florfenicol pharmacokinetics in turkeys
Abstract
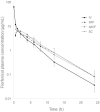
Florfenicol is a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug used in the treatment of farm animals, including poultry. This drug is poorly soluble in water, therefore, administration in drinking water may lead to high variability of concentrations in treated individuals. The use of injection preparations, however, requires individual administration and may have a negative effect on the quality of the carcass. In addition, the renal portal system in birds may reduce the bioavailability of the drug administered in the caudofemoral region of the body. The aim of this study was to compare the pharmacokinetics of florfenicol in turkeys after a single intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous administration at a dose of 15 mg/kg body weight. Additionally, to evaluate the effect of renal portal system on drug kinetics, the intramuscular administration was divided into pectoral and caudofemoral administration. The study showed that the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) was similar regardless of the route of administration. The mean values for clearance and volume of distribution were 0.33 L/kg/h and 0.92 L/kg, respectively. The mean residence time (MRT) was 2.87 h for an intravenous bolus, while for the extravascular administrations it was approx. 5.5 h. The elimination half-life was approx. 4 h regardless of the route of administration. The maximum plasma concentration did not differ statistically between intramuscular (approx. 6.8 mg/L) and subcutaneous (8.2 mg/L) administrations, while the time to appear for this concentration was the longest for caudofemoral administration (1.5 h). The bioavailability was 88.64% for subcutaneous administration, 77.95% for pectoral administration and 85.30% for caudofemoral administration. Overall, all 3 routes of extravascular administration allowed for efficient drug absorption. There was no evidence of an influence of the renal portal system on the kinetic parameters of the drug administered to the lower extremities of the body.
Keywords: florfenicol; pharmacokinetics; renal portal system; site of drug administration; turkey.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative plasma pharmacokinetics and tolerance of florfenicol following intramuscular and intravenous administration to camels, sheep and goats.Vet Res Commun. 2003 Sep;27(6):475-83. doi: 10.1023/a:1025741724701. Vet Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 14582746
-
Comparative pharmacokinetics of florfenicol in the chicken, pigeon and quail.Br Poult Sci. 2009 Jan;50(1):144-9. doi: 10.1080/00071660802613286. Br Poult Sci. 2009. PMID: 19234939
-
Tissue concentrations and pharmacokinetics of florfenicol in broiler chickens.Br Poult Sci. 1997 Sep;38(4):425-8. doi: 10.1080/00071669708418013. Br Poult Sci. 1997. PMID: 9347153
-
Florfenicol pharmacokinetics in lactating cows after intravenous, intramuscular and intramammary administration.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Dec;18(6):413-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.1995.tb00618.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1995. PMID: 8789692 Clinical Trial.
-
Tissue concentrations and pharmacokinetics of florfenicol in broiler chickens.Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1997 May;104(5):178-80. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1997. PMID: 9200888
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol and its metabolite florfenicol amine in the plasma, urine, and feces of fattening male donkeys following single oral administration.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Jan 4;10:1314029. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1314029. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38239747 Free PMC article.
-
The avian respiratory system: implications for anaesthesia.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 Feb 27;380(1920):20230439. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0439. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40010390 Review.
-
In vivo pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study and cutoff of florfenicol against Riemerella anatipestifer in ducks.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104635. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104635. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39647361 Free PMC article.
-
Old Antibiotics Can Learn New Ways: A Systematic Review of Florfenicol Use in Veterinary Medicine and Future Perspectives Using Nanotechnology.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 19;13(10):1695. doi: 10.3390/ani13101695. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics of maropitant citrate in Rhode Island Red chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) following subcutaneous administration.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Sep;45(5):495-500. doi: 10.1111/jvp.13082. Epub 2022 Jun 23. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35734891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abo-EL-Sooud K., Swielim G.A., Khalifa E.F., EL-Gammal S.M. Effect of different sites of intramuscular injection on elimination, bioavailability and tissue residues profile of gentamicin in broiler chickens. Insight Poult. Res. 2012;2:1–7.
-
- Abu-Basha E.A., Gehring R., Al-Shunnaq A.F., Gharaibeh S.M. Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of florfenicol oral solution formulations (FlonicolŪ and VeterinŪ10%) in broiler chickens. J. Bioequivalence Bioavailab. 2012;1:1–5.
-
- Afifi N.A., El-Sooud K.A. Tissue concentrations and pharmacokinetics of florfenicol in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 1997;4:425–428. - PubMed
-
- Anadon A., Martínez M.A., Martinez M., Rios A., Caballero V., Ares I., Martínez-Larrañaga M.R. Plasma and tissue depletion of florfenicol and florfenicol-amine in chickens. Agric. Food Chem. 2008;22:11049–11056. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn R., Prashad D. The avian renal portal system: a model for studying nephrotoxicity of xenobiotics. Toxicol. Lett. 1990;1-2:219–221. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

