MicroRNA-381-3p signatures as a diagnostic marker in patients with sepsis and modulates sepsis-steered cardiac damage and inflammation by binding HMGB1
- PMID: 34784841
- PMCID: PMC8810158
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2006967
MicroRNA-381-3p signatures as a diagnostic marker in patients with sepsis and modulates sepsis-steered cardiac damage and inflammation by binding HMGB1
Abstract
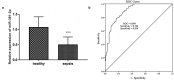
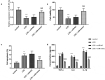
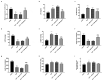
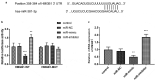
Immune response imbalance and cardiac dysfunction caused by sepsis are the main reasons for death in sepsis. This study aimed to confirm the expression and diagnostic possibility of microRNA-381-3p (miR-381-3p) and its mechanism in sepsis. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) were used to reveal the levels and clinical significance of miR-381-3p. Pearson correlation was conducted to provide the correlations between miR-381-3p and several indexes of sepsis. The H9c2 cell models were constructed by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) was applied to establish the Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat models. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and flow cytometry were the methods to detect the cell viability and death rate of H9c2. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed to evaluate the concentration of inflammatory cytokines. The target gene of miR-381-3p was validated via the luciferase report system. The low expression of miR-381-3p was found in the serum of patients with sepsis. The lessened miR-381-3p could be a marker in the discrimination of sepsis patients. Overexpression of miR-381-3p could repress the mRNA expression of HMGB1, inhibit the cell apoptosis and inflammatory response, and motivate the viability of sepsis cells. At the same time, enhanced miR-381-3p promoted the inhibition of inflammation and cardiac dysfunction in the rat model of sepsis. Collectively, reduced levels of serum miR-381-3p can be used as an index to detect sepsis patients. MiR-381-3p restored the inflammatory response and myocardial dysfunction caused by sepsis via HMGB1.
Keywords: HMGB1; MiR-381-3p; inflammation; myocardial dysfunction; sepsis; viability.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
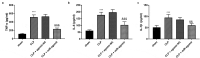
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
