Low cerebrospinal fluid Amyloid-βeta 1-42 in patients with tuberculous meningitis
- PMID: 34784880
- PMCID: PMC8594191
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-021-02468-2
Low cerebrospinal fluid Amyloid-βeta 1-42 in patients with tuberculous meningitis
Abstract
Background: Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is an important disease leading to morbidity, disability and mortality that primarily affects children and immune-depressed patients. Specific neuromarkers predicting outcomes, severity and inflammatory response are still lacking. In recent years an increasing number of evidences show a possible role for infective agents in developing neurodegenerative diseases.
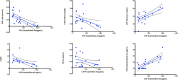
Methods: We retrospectively included 13 HIV-negative patients presenting with TBM and we compared them with two control groups: one of patients with a confirmed diagnosis of AD, and one of those with syphilis where lumbar punctures excluded central nervous system involvement. Lumbar punctures were performed for clinical reasons and CSF biomarkers were routinely available: we analyzed blood brain barrier permeability (CSF to serum albumin ratio, "CSAR"), intrathecal IgG synthesis, (CSF to serum IgG ratio), inflammation (neopterin), amyloid deposition (Aβ1-42), neuronal damage (T-tau, P-tau, 14.3.3) and astrocytosis (S-100 β).
Results: TBM patients were 83 % male and 67 % Caucasian with a median age of 51 years (24.5-63.5 IQR). Apart from altered CSAR (median value 18.4, 17.1-30.9 IQR), neopterin (14.3 ng/ml, 9.7-18.8) and IgG ratios (15.4, 7.9-24.9), patients showed very low levels of Aβ1-42 in their CSF (348.5 pg/mL,125-532.2), even lower compared to AD and controls [603 pg/mL (IQR 528-797) and 978 (IQR 789-1178)]. Protein 14.3.3 tested altered in 38.5 % cases. T-tau, P-tau and S100Beta were in the range of normality. Altered low level of Aβ1-42 correlated over time with classical TBM findings and altered neuromarkers.
Conclusions: CSF Biomarkers from patients with TBM were compatible with inflammation, blood brain barrier damage and impairment in amyloid-beta metabolism. Amyloid-beta could be tested as a prognostic markers, backing the routine use of available neuromarkers. To our knowledge this is the first case showing such low levels of Aβ1-42 in TBM; its accumulation, drove by neuroinflammation related to infections, can be central in understanding neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid-beta; Dementia; Meningitis; Neuromarkers; Tuberculosis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in patients with central nervous system infections: a retrospective study.CNS Spectr. 2020 Jun;25(3):402-408. doi: 10.1017/S1092852919000981. Epub 2019 May 27. CNS Spectr. 2020. PMID: 31130152
-
CSF biomarkers and amyloid PET: concordance and diagnostic accuracy in a MCI cohort.Acta Neurol Belg. 2019 Sep;119(3):445-452. doi: 10.1007/s13760-019-01112-8. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Acta Neurol Belg. 2019. PMID: 30847669
-
Blood brain barrier impairment is associated with cerebrospinal fluid markers of neuronal damage in HIV-positive patients.J Neurovirol. 2016 Feb;22(1):88-92. doi: 10.1007/s13365-015-0371-x. Epub 2015 Aug 6. J Neurovirol. 2016. PMID: 26246357
-
Clinical indications for analysis of Alzheimer's disease CSF biomarkers.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2013 Oct;169(10):709-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2013.07.024. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2013. PMID: 24016466 Review.
-
Biomarkers of Tuberculous Meningitis and Pediatric Human Immunodeficiency Virus on the African Continent.Front Neurol. 2022 May 19;13:793080. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.793080. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35665032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A united model for diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis with random forest and artificial neural network.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 9;14:1094099. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1094099. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36968608 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid and Tau as cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in anti-N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis.Neurol Sci. 2024 Jul;45(7):3399-3410. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07341-x. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38280087
-
Proteins Involved in Synaptic Plasticity Are Downregulated in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Infants With Clinical Sepsis Complicated by Neuroinflammation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 11;16:887212. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.887212. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35634471 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Oxidative Stress in Tuberculosis Meningitis Infection in Diabetics.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 19;11(9):2568. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092568. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37761009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterns of Cerebrospinal Fluid Alzheimer's Dementia Biomarkers in People Living with HIV: Cross-Sectional Study on Associated Factors According to Viral Control, Neurological Confounders and Neurocognition.Viruses. 2022 Apr 4;14(4):753. doi: 10.3390/v14040753. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reiber H, Peter JB. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: disease-related data patterns and evaluation programs. J Neurol Sci. 2001;184(2):101–22. ex 1. - PubMed
-
- Reiber H. Cerebrospinal fluid data compilation and knowledge-based interpretation of bacterial, viral, parasitic, oncological, chronic inflammatory and demyelinating diseases. Diagnostic patterns not to be missed in neurology and psychiatry. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2016;74(4):337–50. doi: 10.1590/0004-282X20160044. - DOI - PubMed

