A paradoxical role for sestrin 2 protein in tumor suppression and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 34784907
- PMCID: PMC8596924
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-02317-9
A paradoxical role for sestrin 2 protein in tumor suppression and tumorigenesis
Abstract
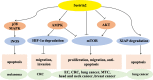
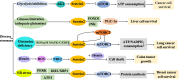
Sestrin 2, a highly conserved stress-induced protein, participates in the pathological processes of metabolic and age-related diseases. This p53-inducible protein also regulates cell growth and metabolism, which is closely related to malignant tumorigenesis. Sestrin 2 was reported to regulate various cellular processes, such as tumor cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis, apoptosis, anoikis resistance, and drug resistance. Although sestrin 2 is associated with colorectal, lung, liver, and other cancers, sestrin 2 expression varies among different types of cancer, and the effects and mechanisms of action of this protein are also different. Sestrin 2 was considered a tumor suppressor gene in most studies, whereas conflicting reports considered sestrin 2 an oncogene. Thus, this review aims to examine the literature regarding sestrin 2 in various cancers, summarize its roles in suppression and tumorigenesis, discuss potential mechanisms in the regulation of cancer, and provide a basis for follow-up research and potential cancer treatment development.
Keywords: Cancer; Sestrin 2; Tumor suppressor; Tumorigenesis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quercetin regulates the sestrin 2-AMPK-p38 MAPK signaling pathway and induces apoptosis by increasing the generation of intracellular ROS in a p53-independent manner.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Apr;33(4):863-9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1658. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24535669 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased expression of sestrin 2 predicts unfavorable outcome in colorectal cancer.Oncol Rep. 2015 Mar;33(3):1349-57. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3701. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25572852
-
Sestrin 2 suppresses cells proliferation through AMPK/mTORC1 pathway activation in colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):49318-49328. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17595. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28525387 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions of sestrin proteins: Insights to clinical therapy.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 18;10(14):e34590. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34590. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39130415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1) in tumorigenesis: overexpression in human cancer, implication in tumorigenesis, oncogenic functions, tumor-suppressive properties, and target of anticancer therapy.Adv Cancer Res. 2013;119:191-419. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407190-2.00016-2. Adv Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23870513 Review.
Cited by
-
Sestrin2-mediated disassembly of stress granules dampens aerobic glycolysis to overcome glucose starvation.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Apr 14;9(1):127. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01411-3. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37059726 Free PMC article.
-
Link of sorafenib resistance with the tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanistic insights.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 22;13:991052. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.991052. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36071839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutrient sensors and their crosstalk.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Jun;55(6):1076-1089. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01006-z. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37258576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Long Noncoding RNAs in Sorafenib Resistance Within Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 21;16(23):3904. doi: 10.3390/cancers16233904. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of sestrins in metabolic and aging-related diseases.Biogerontology. 2024 Feb;25(1):9-22. doi: 10.1007/s10522-023-10053-y. Epub 2023 Jul 30. Biogerontology. 2024. PMID: 37516672 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

