Transdermal Delivery of Telmisartan: Formulation, in vitro, ex vivo, Iontophoretic Permeation Enhancement and Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats
- PMID: 34785889
- PMCID: PMC8590984
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S327860
Transdermal Delivery of Telmisartan: Formulation, in vitro, ex vivo, Iontophoretic Permeation Enhancement and Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to prepare telmisartan transethosomes, incorporate them into a gel, evaluate them for in vitro drug release and in vivo permeation using iontophoresis to enhance their transdermal delivery.
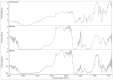
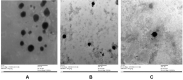
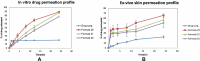
Materials and methods: TE formulae were prepared using various surfactants (SAAs), different ethanol concentrations, and different phospholipid-to-SAA ratios with different cholesterol ratios, characterized according to their entrapment efficiency percentage (EE%), zeta potential (ZP), particle size (PS), and polydispersity index (PDI). The optimum three formulae were incorporated into a gel, evaluated physically, in vitro dissolution, and ex vivo drug permeation using rat skin and Iontophoresis was performed on the best formula.
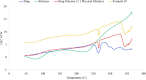
Results: The optimum three formulae (F29, F31, F32) had an EE% of 97±0.26%, 89±0.25% and 88±0.17%, PS of 244±5.88 nm, 337±4.6 nm and 382.2±3.06 nm, PDI of 0.57±1.9, 0.5±1.4 and 0.63±2.2 and ZP of -31.6±1.59 mV, -28.3±3.79 mV and -31±5.65, respectively. Selecting F29 for in vivo study by iontophoretic enhancement, Cmax was increased by 1.85 folds compared to the commercial oral tablet and by 1.5 folds compared to transdermal gel. Tmax decreased by half using iontophoresis compared to commercial tablets and transdermal gel.
Conclusion: The transethosomal formulation of telmisartan enhanced its transdermal absorption and increased its bioavailability as well. Iontophoresis was used to increase maximum plasma concentration and reduce Tmax by half.
Keywords: EE; TEL; entrapment efficiency; iontophoresis; telmisartan; transethosomes.
© 2021 Teaima et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Yasser M, Teaima M, El-Nabarawi M, El-Monem RA. Cubosomal based oral tablet for controlled drug delivery of telmisartan: formulation, in-vitro evaluation and in-vivo comparative pharmacokinetic study in rabbits. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019;45(6):981–994. doi:10.1080/03639045.2019.1590392 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

