A review on the molecular basis underlying the protective effects of Andrographis paniculata and andrographolide against myocardial injury
- PMID: 34785890
- PMCID: PMC8591231
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S331027
A review on the molecular basis underlying the protective effects of Andrographis paniculata and andrographolide against myocardial injury
Abstract
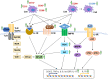
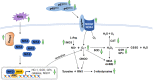
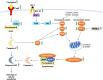
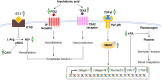
Andrographolide is the major compound found in the medicinal plant, Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees, which accounts for its medicinal properties. Both the plant extract and compound have been reported to exhibit potential cardiovascular activities. This review summarises related studies describing the biological activities and target mechanisms of A. paniculata and andrographolide in vivo and in vitro. The current evidence unambiguously indicated the protective effects provided by A. paniculata and andrographolide administration against myocardial injury. The intervention ameliorates the symptoms of myocardial injury by interfering with the inductive phase of a) inflammatory response mediated by nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signalling molecules; b) oxidative stress via activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf-2) and reduction of enzymes responsible for generating reactive oxygen and nitrogen species; c) intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms in apoptosis regulated by upstream insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-α); d) profibrotic growth factors thus reducing cardiac fibrosis, improving endothelial function and fibrinolytic function. In conclusion, A. paniculata and andrographolide possess therapeutic potential in the management of myocardial injury, which requires further validation in human clinical trials.
Keywords: Andrographis; apoptosis; fibrosis; inflammation; myocardial infarction; oxidative stress.
© 2021 Wong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Khan I, Khan F, Farooqui A, et al. Andrographolide exhibits anticancer potential against human colon cancer cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and programmed cell death via augmentation of intracellular reactive oxygen species level. Nutr Cancer. 2018;70:787–803. doi:10.1080/01635581.2018.1470649 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

