Dynamic Urinary Proteome Changes in Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma Mouse Model Using Data-Independent Acquisition Proteomics
- PMID: 34785909
- PMCID: PMC8590963
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S330054
Dynamic Urinary Proteome Changes in Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma Mouse Model Using Data-Independent Acquisition Proteomics
Abstract
Background: In this work, we aim to investigate dynamic urinary proteome changes during asthma development and to identify potential urinary protein biomarkers for the diagnosis of asthma.
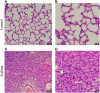
Methods: An ovalbumin (OVA)-induced mouse model was used to mimic asthma. The urinary proteome from asthma and control mice was determined using data-independent acquisition combined with high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry.
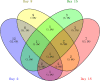
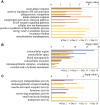
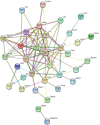
Results: Overall, 331 proteins were identified, among which 53 were differentially expressed (26, 24, 14 and 20 on days 2, 8, 15 and 18, respectively; 1.5-fold change, adjust P<0.05). Gene Ontology annotation of the differential proteins showed that the acute-phase response, innate immune response, B cell receptor signaling pathway, and complement activation were significantly enriched. Protein-protein interaction network revealed that these differential proteins were partially biologically connected in OVA-induced asthma, as a group. On days 2 and 8, after two episodes of OVA sensitization, six differential proteins (CRAMP, ECP, HP, F2, AGP1, and CFB) were also reported to be closely associated with asthma. These proteins may hold the potential for the early screening of asthma. On days 15 and 18, after challenged with 1% OVA by inhalation, seven differential proteins (VDBP, HP, CTSE, PIGR, AAT, TRFE, and HPX) were also reported to be closely associated with asthma. Thus, these proteins hold the potential to be biomarkers for the diagnosis of asthma attack.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that the urinary proteome could reflect dynamic pathophysiological changes in asthma progression.
Keywords: OVA-induced asthma; data-independent acquisition; mice; proteome; urine.
© 2021 Qin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proteome Analysis of Urinary Biomarkers in a Bovine IRBP-Induced Uveitis Rat Model via Data-Independent Acquisition and Parallel Reaction Monitoring Proteomics.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 22;9:831632. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.831632. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35274006 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-Associated Proteins Are Enriched in Lung Tissue-Derived Extracellular Vesicles during Allergen-Induced Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4718. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094718. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946872 Free PMC article.
-
[Prediction of Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Asthma Based on Proteomics of Mouse Lung Tissue].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022 Dec;44(6):961-969. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.14667. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 36621785 Chinese.
-
Comparison of asthma phenotypes in OVA-induced mice challenged via inhaled and intranasal routes.BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Dec 10;19(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-1001-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2019. PMID: 31823765 Free PMC article.
-
TMT-based quantitative proteomics reveals suppression of SLC3A2 and ATP1A3 expression contributes to the inhibitory role of acupuncture on airway inflammation in an OVA-induced mouse asthma model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Feb;134:111001. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111001. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33341053
Cited by
-
Quantitative urinary proteome analysis reveals potential biomarkers for disease activity of Behcet's disease uveitis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12886-024-03557-9. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38982370 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of electroacupuncture on global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: A urine proteome analysis.Brain Behav. 2024 Jan;14(1):e3382. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3382. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 38376040 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Proteome and Exosome Analysis Protocol for the Discovery of Respiratory Diseases Biomarkers.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 3;15(1):60. doi: 10.3390/biom15010060. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 39858454 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome analysis of urinary biomarkers in a cigarette smoke-induced COPD rat model.Respir Res. 2022 Jun 15;23(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02070-1. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 35705945 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

