ARNTL2 is a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlates with Immune Cell Infiltration in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 34785930
- PMCID: PMC8591114
- DOI: 10.2147/PGPM.S331431
ARNTL2 is a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlates with Immune Cell Infiltration in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive breast cancer subtype and is associated with poor prognosis. The aberrant expression of circadian genes contributes to the origin and progression of breast cancer. The present study was designed to explore the potential function and prognosis value of circadian genes in TNBC.
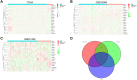
Methods: The transcriptome data of circadian genes were downloaded from The Cancer Genomic Atlas (TCGA), GSE25066 and GSE31448 datasets. The differential expressed circadian genes between non-TNBC and TNBC patients were analysed by Wilcoxon test. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were employed to identify the prognostic circadian genes. Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) were performed to study the biological functions of ARNTL2. The composition of 22 immune cells in the tumour samples was estimated with CIBERSORT algorithm. The correlations between ARNTL2 expression and tumour-infiltrating immune cells were evaluated by Spearman correlation coefficient.
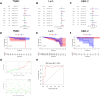
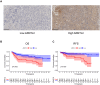
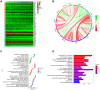
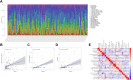
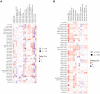
Results: A total of 8 circadian genes were found to be differentially expressed between non-TNBC and TNBC, but only ARNTL2 has prognostic value. Multivariate Cox analysis identified that ARNTL2 was an independent prognosis factor for overall survival and relapse-free survival in TNBC patients. Functionally, ARNTL2 was mainly involved in immune response processes such as positive regulation of cytokine production, regulation of innate immune response, and cellular responses to molecules of bacterial origin. High expression of ARNTL2 was positively correlated with activated CD4 memory T cells, activated mast cells, and neutrophil infiltration and the expression of markers of neutrophils (ITGAM), dendritic cells (HLA-DRA, HLA-DPA1, ITGAM), Th1 (IL1B, STAT1), Th2 (IL13), Th17 (STAT3) and mast cells (TPSB2, TPSAB1).
Conclusion: ARNTL2 may be linked with the functional modulation of the tumour immune microenvironment and serve as a potential biomarker for predicting the prognosis of TNBC patients.
Keywords: ARNTL2; biomarker; circadian rhythm; immune cell infiltration; triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2021 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Screening of DNA Damage Repair Genes Involved in the Prognosis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Based on Bioinformatics.Front Genet. 2021 Aug 2;12:721873. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.721873. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34408776 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity and Extracellular Matrix Characteristics of Breast Cancer Subtypes Based on Identification by T Helper Cells Profiling.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 20;13:859581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.859581. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35795662 Free PMC article.
-
The analysis of gene co-expression network and immune infiltration revealed biomarkers between triple-negative and non-triple negative breast cancer.Front Genet. 2025 Jan 6;15:1505011. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1505011. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 39834541 Free PMC article.
-
Identify potential prognostic indicators and tumor-infiltrating immune cells in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2022 Feb 25;42(2):BSR20212523. doi: 10.1042/BSR20212523. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35083488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding and harnessing triple-negative breast cancer-related microbiota in oncology.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 24;12:1020121. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1020121. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36505861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A circadian rhythm-related gene signature for prognosis, invasion and immune microenvironment of breast cancer.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 5;13:1104338. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1104338. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36685904 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of COVID-19 transcriptional signatures between clinical samples and preclinical cell models in the search for disease master regulators and drug repositioning candidates.Virus Res. 2023 Mar;326:199053. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199053. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 36709793 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a novel prognostic signature for cutaneous melanoma based on ferroptosis-related genes.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 24;9(5):e15725. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15725. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37159694 Free PMC article.
-
ARNTL2: a key player in promoting tumor aggressiveness in papillary thyroid cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 31;14(1):522-534. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1205. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39974412 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian disruption: from mouse models to molecular mechanisms and cancer therapeutic targets.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Mar;42(1):297-322. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10072-0. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 36513953 Review.
References
-
- Hwang S, Park S, Kwon Y. Recent therapeutic trends and promising targets in triple negative breast cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;199:30–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

