Simple and Unbiased OSA Prescreening: Introduction of a New Morphologic OSA Prediction Score
- PMID: 34785967
- PMCID: PMC8590840
- DOI: 10.2147/NSS.S333471
Simple and Unbiased OSA Prescreening: Introduction of a New Morphologic OSA Prediction Score
Abstract
Purpose: An early prescreening in suspected obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients is desirable to expedite diagnosis and treatment. However, the accuracy and applicability of current prescreening tools is insufficient. We developed and tested an unbiased scoring system based solely on objective variables, which focuses on the diagnosis of severe OSA and exclusion of OSA.
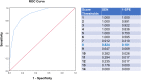
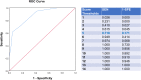
Patients and methods: The OSA prediction score was developed (n = 150) and validated (n = 50) within German sleep center patients that were recruited as part of the Sleep Apnea Global Interdisciplinary Consortium (SAGIC). Six objective variables that were easy to assess and highly correlated with the apnea-hypopnea index were chosen for the score, including some known OSA risk factors: body-mass index, neck circumference, waist circumference, tongue position, male gender, and age (for women only). To test the predictive ability of the score and identify score thresholds, the receiver-operating characteristics (ROC) and curve were calculated.
Results: A score ≥8 for predicting severe OSA resulted in an area under the ROC curve (ROC-AUC) of 90% (95% confidence interval: 84%, 95%), test accuracy of 82% (75%, 88%), sensitivity of 82% (65%, 93%), specificity of 82% (74%, 88%), and positive likelihood ratio of 4.55 (3.00, 6.90). A score ≤5 for predicting the absence of OSA resulted in a ROC-AUC of 89% (83%, 94%), test accuracy of 80% (73%, 86%), sensitivity of 72% (55%, 85%), specificity of 83% (75%, 89%), and positive likelihood ratio of 4.20 (2.66, 6.61). Performance characteristics were comparable in the small validation sample.
Conclusion: We introduced a novel prescreening tool combining easily obtainable objective measures with predictive power and high general applicability. The proposed tool successfully predicted severe OSA (important due to its high risk of cardiovascular disease) and the exclusion of OSA (rarely a feature of previous screening instruments, but important for better differential diagnosis and treatment).
Keywords: diagnostic; obstructive sleep apnea; screening; sensitivity; specificity.
© 2021 Laharnar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Outside the submitted work, PAC has an appointment to an endowed academic Chair at the University of Sydney that was created from ResMed funding. He receives no personal fees and this relationship is managed by an Oversight Committee of the University. He has received research support from ResMed, SomnoMed, Zephyr Sleep Technologies, and Bayer. He is a consultant/adviser to Zephyr Sleep Technologies, Signifier Medical Technologies, SomnoMed, ResMed, and Bayer. He has a pecuniary interest in SomnoMed related to a previous role in R&D (2004). AIP is the John Miclot Professor of Medicine. Funds for this endowment are provided by the Phillips Respironics Foundation. RS reports grants from ResMed, Inspire, CryOSA; he is on the Advisory Board for eXciteOSA and has royalties from UptoDate and Merck Manual, outside the submitted work. IF has received research grants from Löwenstein, ResMed, Weinmann and Philips at the Charite University Hospital. TP reports grants from Cidelec, grants and personal fees from Löwenstein Medical, grants from Novartis, personal fees from Jazz Pharma, Bayer Healthcare, Cerebra, Philips, and Neuwirth, speaker fee from National Sleep Foundation, outside the submitted work; and shareholder of Advanced Sleep Research, The Siestagroup GmbH, Nukute. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validation of NoSAS (Neck, Obesity, Snoring, Age, Sex) score as a screening tool for obstructive sleep apnea: Analysis in a sleep clinic.Pulmonology. 2019 Sep-Oct;25(5):263-270. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2019.04.004. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Pulmonology. 2019. PMID: 31196834
-
[Validation of NoSAS Score and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome Screening Model for Female Snorers in Females with Obstructive Sleep Apnea].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2019 Dec 30;41(6):825-831. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.11131. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31907135 Chinese.
-
Age, gender, neck circumference, and Epworth sleepiness scale do not predict obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): The challenge to predict OSA in advanced COPD.PLoS One. 2017 May 16;12(5):e0177289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177289. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28510598 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of clinical scoring tools for the diagnosis of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea.Laryngoscope. 2020 Apr;130(4):1034-1043. doi: 10.1002/lary.28146. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Laryngoscope. 2020. PMID: 31233218 Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG, STOP, and Epworth sleepiness scale in detecting obstructive sleep apnea: A bivariate meta-analysis.Sleep Med Rev. 2017 Dec;36:57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Sleep Med Rev. 2017. PMID: 27919588 Review.
Cited by
-
Orofacial Pain and Snoring/Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Individuals with Head and Neck Cancer: A Critical Review.J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2022 Spring;36(2):85-102. doi: 10.11607/ofph.3176. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2022. PMID: 35943322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neck circumference predicts the incident cardiac events of obese hypertension with obstructive sleep apnea.Am J Prev Cardiol. 2025 Jun 19;23:101048. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2025.101048. eCollection 2025 Sep. Am J Prev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40672874 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Application Evaluation of an Improved Obstructive Sleep Apnea Screening Questionnaire for Chinese Community: The CNCQ-OSA.Nat Sci Sleep. 2023 Mar 13;15:103-114. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S396695. eCollection 2023. Nat Sci Sleep. 2023. PMID: 36937783 Free PMC article.
-
"The M-APNE score: an objective screening tool for OSA highlighting the area under the inspiratory flow-volume curve".Sleep Breath. 2025 Jan 14;29(1):77. doi: 10.1007/s11325-024-03239-2. Sleep Breath. 2025. PMID: 39808237
-
Oxygen regulated protein 150 can be considered as a severity indicator in obstructive sleep apnea.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 18;15(1):26107. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99987-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40681769 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

