LncRNA SNHG4 promotes malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the miR-144-3p/MET axis
- PMID: 34786048
- PMCID: PMC8581836
LncRNA SNHG4 promotes malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the miR-144-3p/MET axis
Abstract
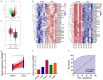
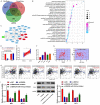
Objective: This study aimed to explore the underlying mechanism of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) SNHG4 regulating MET to participate in the malignant biologic behaviors and immune escape of colorectal cancer (CRC) by sponging miR-144-3p.
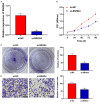
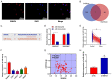
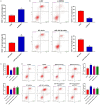
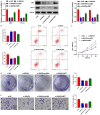
Methods: CRC tissues were collected and the expression levels of lncRNA SNHG4, miR-144-3p, and MET were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Then, the localization of lncRNA SNHG4 was studied by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and the regulatory relationship among lncRNA SNHG4, miR-144-3p, and MET was verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Next, cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), Clone formation assay, and Transwell migration assay were carried out to evaluate cell proliferation, colony formation, and invasion, respectively. Flow cytometry was performed to evaluate cell apoptosis. Western blotting was applied to semi-quantify the expression levels of MET and PD-L1 in cells.
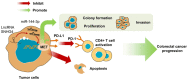
Results: LncRNA SNHG4 expression was upregulated in CRC tissues. Knockdown of lncRNA SNHG4 suppressed the proliferation, colony formation and invasion of CRC cells (all P<0.05). LncRNA SNHG4 directly regulated miR-144-3p, by which either lncRNA SNHG4 knockdown or miR-144-3p overexpression can inhibit CD4+ T cell apoptosis (both P<0.05) to suppress immune escape. Either overexpression of lncRNA SNHG4 or knockdown of miR-144-3p activated PD-1/PD-L1 and induced CD4+ T cell apoptosis (both P<0.05). LncRNA SNHG4 targeted and regulated MET through the regulation of miR-144-3p, while overexpression of MET can partially reverse the effect of lncRNA SNHG4 knockdown on CD4+ T cells.
Conclusion: LncRNA SNHG4 sponges miR-144-3p and upregulates MET to promote the proliferation, colony formation, invasion, and immune escape of CRC cells, leading to the progression of CRC.
Keywords: LncRNA SNHG4; MET; colorectal cancer; immune escape; miR-144-3p.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
lncRNA SNHG4 modulates colorectal cancer cell cycle and cell proliferation through regulating miR-590-3p/CDK1 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Mar 19;13(7):9838-9858. doi: 10.18632/aging.202737. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33744866 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA SNHG4 enhanced gastric cancer progression by modulating miR-409-3p/CREB1 axis.Oncol Res. 2024 Dec 20;33(1):185-198. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.042281. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39735673 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA SNHG4 promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating c-Met via targeting miR-148a-3p.Cell Cycle. 2019 Dec;18(23):3313-3324. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1674071. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Cell Cycle. 2019. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2023 Jul-Aug;22(14-16):1803. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2211864. PMID: 31590627 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
LncRNA SNHG4 promotes tumour growth by sponging miR-224-3p and predicts poor survival and recurrence in human osteosarcoma.Cell Prolif. 2018 Dec;51(6):e12515. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12515. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Cell Prolif. 2018. PMID: 30152090 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Mechanisms and Clinical Significance of Lnc SNHG4 in Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(44):3563-3571. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221121161950. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 36411578 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs as regulators of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy: targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Mar 10;24(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03293-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38462628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs: regulators of autophagy and potential biomarkers in therapy resistance and urological cancers.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 24;15:1442227. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1442227. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39512820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Coding RNAs Implicated in the Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer: Roles, Mechanisms and Clinical Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 28;12:888276. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.888276. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35574420 Free PMC article.
-
Association between small nucleolar RNA host gene expression and survival outcome of colorectal cancer patients: A meta-analysis based on PRISMA and bioinformatics analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 20;13:1094131. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1094131. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36895488 Free PMC article.
-
SnoRNA and lncSNHG: Advances of nucleolar small RNA host gene transcripts in anti-tumor immunity.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 15;14:1143980. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1143980. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
