Stapled trans-anal rectal resection can improve constipation symptoms and inflammatory reaction of patients with outlet obstructive constipation
- PMID: 34786073
- PMCID: PMC8581840
Stapled trans-anal rectal resection can improve constipation symptoms and inflammatory reaction of patients with outlet obstructive constipation
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of stapled trans-anal rectal resection (STARR) on constipation symptoms and inflammatory reaction in patients with outlet obstructive constipation (OOC).
Methods: From January 2019 to June 2020, a retrospective analysis was conducted on the medical data of 124 patients with OOC admitted to our hospital. According to the different surgical methods, sixty patients were assigned to the control group (CG) treated with Bresler operation, and sixty-four patients were included in the research group (RG) receiving STARR. The total effective rate of treatment, the incidence of postoperative complications, and mid- and long-term recurrence rate were observed between the two groups. The anorectal dynamic indexes, the constipation scoring system (CSS), obstructive defecation syndrome (ODS), visual analogue scale (VAS) scores, and the changes of inflammatory cytokine [tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6)] were compared between the two groups, and the perioperative indexes were observed.
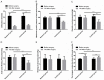
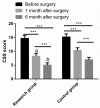
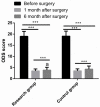
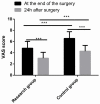
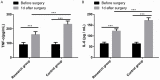
Results: After operation, a remarkably higher total effective rate was observed in the RG as compared to the CG. The RG obtained lower results in terms of the incidence of postoperative complications, 3-year recurrence rate, operation cost, and intraoperative blood loss than CG. Compared with patients in the CG, those in the RG had shorter operation time, first exhaust time, time of leaving bed, and hospitalization time. Moreover, a shorter defecation time of patients in the RG was also obtained 14 days after treatment. In addition to rectal rest pressure that was similar between the two groups, the anal maximal contraction pressure, anal longest contraction time, anorectal relaxation pressure, and anal rest pressure were significantly higher in the RG than in the CG. After operation, remarkably lower CSS and ODS scores of patients were obtained in the RG than in the CG. The RG yielded lower VAS scores after operation and 24 hours after operation, and lower levels of TNF-α and IL-6 1 day after operation in contrast to the CG.
Conclusion: STARR can effectively improve the clinical efficacy, ameliorate the symptoms of postoperative constipation, reduce the long-term recurrence rate, relieve postoperative pain, and better protect the anorectal function and mitigate inflammatory reaction for patients with obstructive constipation.
Keywords: Stapled trans-anal rectal resection; constipation symptoms; inflammatory reaction; outlet obstructive constipation.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Modified stapled transanal rectal resection combined with perioperative pelvic floor biofeedback therapy in the treatment of obstructed defecation syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 May 25;20(5):514-518. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28534327 Chinese.
-
[Efficacy observation of partial stapled transanal rectal resection combined with Bresler procedure in the treatment of rectocele and internal rectal intussusception].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 May;19(5):566-70. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27215528 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
New trends in the surgical treatment of outlet obstruction: clinical and functional results of two novel transanal stapled techniques from a randomised controlled trial.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004 Jul;19(4):359-69. doi: 10.1007/s00384-003-0572-2. Epub 2004 Mar 13. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004. PMID: 15024596 Clinical Trial.
-
Stapled Transanal Rectal Resection (Starr) in the Treatment of Obstructed Defecation: A Systematic Review.Front Surg. 2022 Feb 14;9:790287. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.790287. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35237648 Free PMC article.
-
Relief of obstructed defecation syndrome after stapled transanal rectal resection (STARR): a meta-analysis.Acta Chir Belg. 2014 May-Jun;114(3):189-97. doi: 10.1080/00015458.2014.11681007. Acta Chir Belg. 2014. PMID: 25102709 Review.
Cited by
-
Value of Defecography in the Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of the Modified Wells Procedure for Rectal Prolapse.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Apr 10;2022:2219330. doi: 10.1155/2022/2219330. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. Retraction in: Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9847620. doi: 10.1155/2023/9847620. PMID: 35480080 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Shin JE, Park KS, Nam K. Chronic functional constipation. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;73:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Vriesman MH, Koppen IJN, Camilleri M, Di Lorenzo C, Benninga MA. Management of functional constipation in children and adults. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17:21–39. - PubMed
-
- Sharma A, Rao S. Constipation: pathophysiology and current therapeutic approaches. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;239:59–74. - PubMed
-
- Rao SS, Rattanakovit K, Patcharatrakul T. Diagnosis and management of chronic constipation in adults. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:295–305. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
