Metabolic and biophysical study of the MFN2Ile213Thr mutant causing Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathy (HMSN)
- PMID: 34786076
- PMCID: PMC8581889
Metabolic and biophysical study of the MFN2Ile213Thr mutant causing Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathy (HMSN)
Abstract
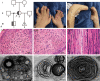
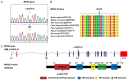
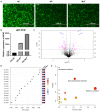
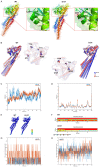
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) 2A disease, a genetic axonal nervous lesion, results from MFN2 pathogenic variation, and this gene plays a pivotal role in mitochondrial dynamics and calcium signaling. However, the underlying mechanism linking MFN2 defect to progressive dying-back of peripheral nerves is still unclear. The present work focused on analyzing one CMT2A patient from multiple perspectives. Clinical and pathologic evaluation was initially conducted on the recruited case. Subsequently, Sanger sequencing and whole-exome sequencing (WES) were performed for genetic detection. To reveal the cell metabolic alteration caused by the identified variant, this study also established and transfected plasmid vectors in HEK293 cells and analyzed cell metabolites through liquid chromatography in combination with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC Q-TOF MS). Additionally, we completed structural modeling and molecular dynamic (MD) simulation to investigate the intramolecular impact of the variant. According to our results, the clinical and neuropathologic manifestations of the proband matched with the diagnosis of CMT. The causative variant MFN2: c.638T>C: (p.Ile213Thr) was identified through genetic analysis. Moreover, metabolic pathway enrichment results demonstrated that this variant significantly affected the metabolism of sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids. MD analysis indicated that this variant crippled the binding ability of MFN2 to GTP. Taken together, our study deduced preliminary clues for the underlying mechanism by which mutant MFN2 affects cell metabolism and provided a novel perspective to understand the cellular and molecular impacts of MFN2 variants.
Keywords: CMT2A; MFN2; hereditary neuropathy; metabonomics; molecular dynamic simulation; whole-exome sequencing.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early onset severe and late-onset mild Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease with mitofusin 2 (MFN2) mutations.Brain. 2006 Aug;129(Pt 8):2103-18. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl174. Epub 2006 Jul 10. Brain. 2006. PMID: 16835246
-
Genetic epidemiology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2012;(193):iv-22. doi: 10.1111/ane.12013. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2012. PMID: 23106488
-
Exome sequencing reveals a novel MFN2 missense mutation in a Chinese family with Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2A.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Sep;16(3):2281-2286. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6513. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30210586 Free PMC article.
-
An integrative analysis of genotype-phenotype correlation in Charcot Marie Tooth type 2A disease with MFN2 variants: A case and systematic review.Gene. 2023 Oct 20;883:147684. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147684. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Gene. 2023. PMID: 37536398
-
Role of mitofusin 2 mutations in the physiopathology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A.Exp Neurol. 2009 Aug;218(2):268-73. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.05.003. Epub 2009 May 8. Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19427854 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Impaired Mitochondrial Dynamics in MFN2-Mediated Pathology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 24;10:858286. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.858286. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35399520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nagappa M, Sharma S, Taly AB. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Charcot Marie Tooth. - PubMed
-
- Laurá M, Singh D, Ramdharry G, Morrow J, Skorupinska M, Pareyson D, Burns J, Lewis RA, Scherer SS, Herrmann DN, Cullen N, Bradish C, Gaiani L, Martinelli N, Gibbons P, Pfeffer G, Phisitkul P, Wapner K, Sanders J, Flemister S, Shy ME, Reilly MM Inherited Neuropathies Consortium. CMT subtypes and disease burden in patients enrolled in the Inherited Neuropathies Consortium natural history study: a cross-sectional analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86:873–878. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Laura M, Pipis M, Rossor AM, Reilly MM. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related disorders: an evolving landscape. Curr Opin Neurol. 2019;32:641–650. - PubMed
-
- Bergamin G, Boaretto F, Briani C, Pegoraro E, Cacciavillani M, Martinuzzi A, Muglia M, Vettori A, Vazza G, Mostacciuolo ML. Mutation analysis of MFN2, GJB1, MPZ and PMP22 in Italian patients with axonal charcot-marie-tooth disease. Neuromol Med. 2014;16:540–550. - PubMed
-
- Züchner S. MFN2 Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathy. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Mirzaa G, Amemiya A, editors. Seattle: Seattle (WA), University of Washington; 2020. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
